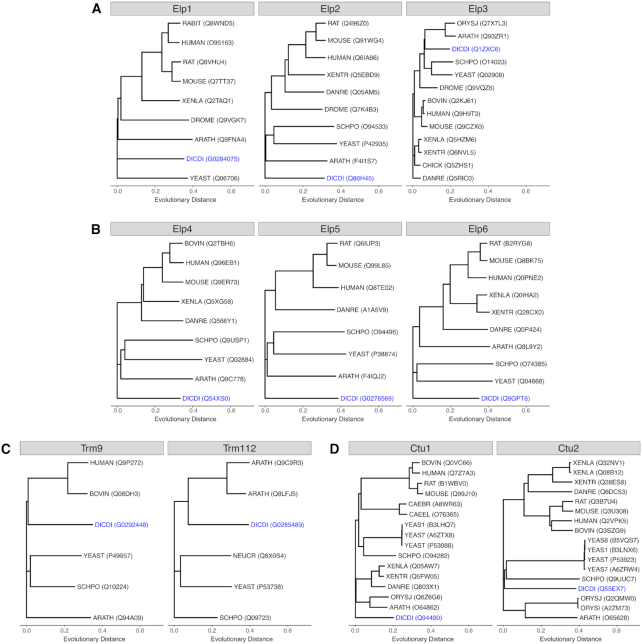
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic trees of proteins acting in the Elongator-dependent tRNA modification pathway. Shown are the trees for proteins identified as homologues of the proteins Elp1-Elp3 (A), Elp4-Elp6 (B), Trm9 and Trm112 (C) and Ctu1 and Ctu2 (D). Protein sequences of the following species were compared (where available): ARATH: Arabidopsis thaliana; BOVIN: Bos taurus; CAEBR: Caenorhabditis briggsae; CAEEL: Caenorhabditis elegans; CHICK: Gallus gallus; CHLRE: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; DANRE: Danio rerio; DICDI: Dictyostelium discoideum; DROME: Drosophila melanogaster; HUMAN: Homo sapiens; MAIZE: Zea mays; MOUSE: Mus musculus; NEUCR: Neurospora crassa (strain ATCC 24698/74-OR23-1A/CBS 708.71/DSM 1257/FGSC 987); ORYSI: Oryza sativa subsp. indica; ORYSJ: Oryza sativa subsp. japonica; RABIT: Oryctolagus cuniculus; RAT: Rattus norvegicus; SCHPO: Schizosaccharomyces pombe (strain 972/ATCC 24843); XENLA: Xenopus laevis; XENTR: Xenopus tropicalis; YEAS1: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain RM11-1a); YEAS6: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain AWRI1631); YEAS7: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain YJM789); YEAST: Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508/S288c). Their relative evolutionary distances (unitless) are plotted using the same scale for all proteins and their UniprotKB or Dictybase identifiers are given in brackets. D. discoideum homologues are shown in blue.