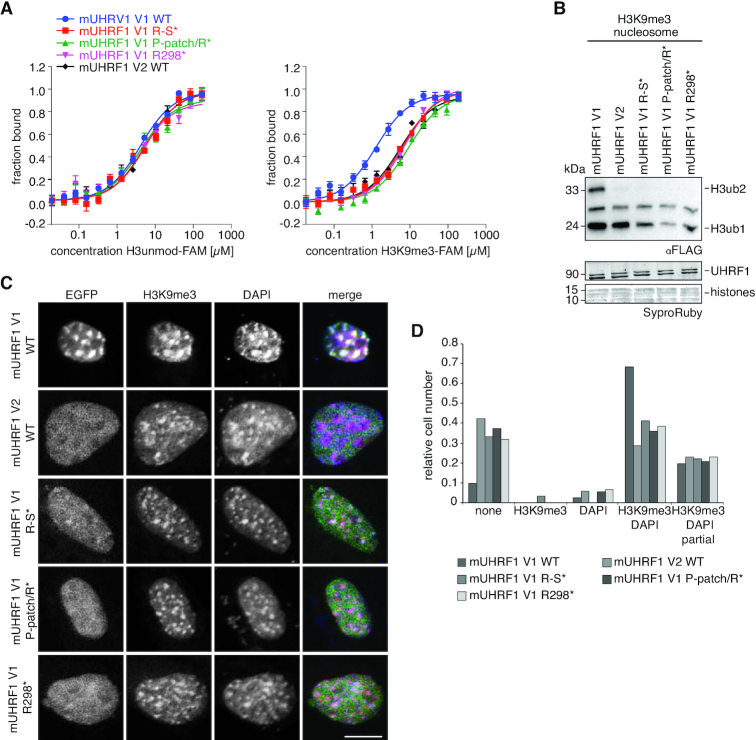
Figure 7.
The insertion of mLinker 2 V1 facilitates synergistic H3K9me3-recognition by the mTTD-PHD V1 module. (A) Titration series of recombinant mUHRF1 V1 WT, R298A (R298*), P293A/P294A/P295A (P-patch*), P293A/P294A/P295A/L297A/R298A (P-patch/R*), R298A/N299A/T300A/G301A/K302A/S303A (R-S*) and mUHRF1 V2 WT with H3 unmodified- (left) and H3K9me3-FAM (right) peptides were analysed by microscale thermophoresis. Data are plotted as average of three independent experiments; error bars correspond to s.d. (B) The recombinant proteins of (A) were subjected to E3 ubiquitin ligase assays using recombinant H3K9me3 mononucleosomes. Reactions were analysed by western blotting (top). Signals for UHRF1 and histone proteins on the stained western blot membrane are shown for loading controls (bottom). Running positions of molecular weight markers (left) and different identified proteins (right) are indicated. (C) Representative confocal images of murine NIH-3T3 cells expressing different EGFP-tagged mUHRF1 V1 and V2 WT and mutant proteins (EGFP, green channel). Immunofluorescence staining was performed for H3K9me3 (red channel). DAPI staining marks the DNA (blue channel). Merged images show all three channels simultaneously. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Co-localization of EGFP-tagged proteins as shown in (C) with H3K9me3 and DAPI-dense regions was assessed visually and is plotted relative to the total number of EGFP-positive cells (n > 70).