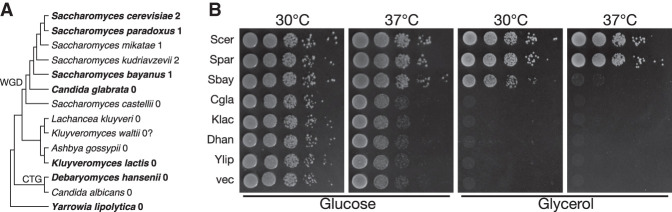
FIGURE 4.
Compatibility of yeast Dmr1p orthologs with S. cerevisiae mtDNA correlates with the presence of the (AUA)4AU recognition motifs in the 15S rRNA sequence. (A) Cladogram representing the phylogeny of 14 selected representatives of Saccharomycetales based on the published fungal maximum likelihood tree (Fitzpatrick et al. 2006). DMR1 orthologs from species in bold type were tested for compatibility in this work (S. mikatae and S. kudriavzevii were also found compatible in Jhuang et al. 2017). Numbers denote the occurrences of the (AUA)4AU motif in 15S rRNA sequences of each species. (WGD) Whole genome duplication, (CTG) the clade with nonstandard nuclear genetic code (CTG encodes serine). The sequence from K. waltii was not complete, which is denoted by the question mark. (B) Respiratory competence of Δdmr S. cerevisiae strains expressing DMR1 orthologs from S. paradoxus (Spar), S. bayanus (Sbay), C. glabrata (Cgla), Kluyveromyces lactis (Klac), Debaryomyces hansenii (Dhan), and Yarrowia lipolytica (Ylip). The S. cerevisiae (Scer) DMR1 gene was used as a positive control, and the empty vector was used as a negative control (vec). Overnight cultures in complete synthetic medium (CSM) without leucine were spotted in a series of 10-fold dilutions, on fermentable (glucose) and respiratory (glycerol) media and incubated at 30°C (normal) and 37°C (restrictive) for 3 d.