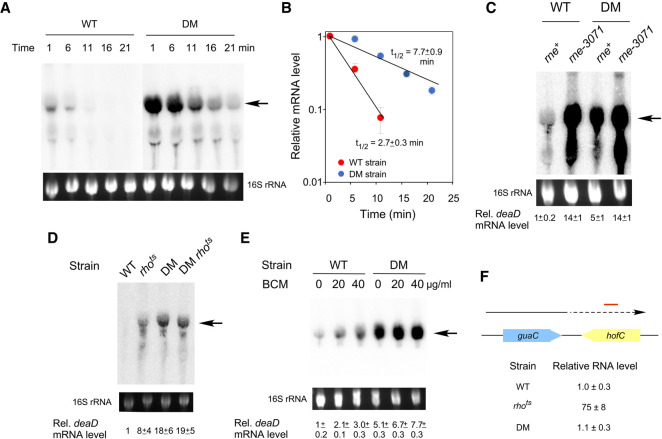
FIGURE 3.
Autoregulation of deaD is mediated via mRNA stability and transcription termination. (A) Northern-blot analysis. WT or DM strains were treated with rifampicin and aliquots of the cell cultures were harvested at different times after rifampicin addition, as indicated at the top. Total RNA was prepared from these cultures and analyzed by Northern blot using a probe for deaD mRNA. (B) Half-life analysis. The levels of deaD mRNA from (A) were normalized and plotted as a function of time after rifampicin addition on a semi-logarithmic scale. Each data point represents an average value from three experiments. The calculated half-life of the deaD mRNA in each strain is indicated. (C) Inactivation of RNase E increases deaD mRNA levels. WT and DM strains, as well as their rne-3071 derivatives, were transferred to 42°C for 30 min after growth to mid-log phase at 30°C, followed by harvesting of cultures, RNA preparation and Northern blot analysis. (D) Effects of Rho inactivation on deaD mRNA. WT or DM strains containing either wild-type rho or a rhots allele were grown to mid-log phase at 30°C and then transferred to 42°C for 30 min before harvesting. RNA was isolated from the strains and analyzed by Northern blotting. (E) Effect of BCM addition on deaD mRNA. Cultures of WT or DM strains were grown at 37°C and were either untreated or treated with 20 or 40 µg/mL of BCM for 20 min before harvesting. RNA was isolated from the strains and analyzed by Northern blotting. (F) RNA was isolated from WT, rhots or DM strains after growth at 42°C for 30 min and the levels of RNA transcription from 538 to 638 bp downstream from the guaC coding region were quantified by qRT-PCR. The convergently oriented guaC and hofC coding regions are shown in blue and yellow, respectively. The arrow depicts transcription from the guaC promoter with dotted lines indicating readthrough antisense transcription into the hofC coding region. The region analyzed by qRT-PCR is indicated by a red line.