Fig 3. Skeletal muscle ultrastructure.
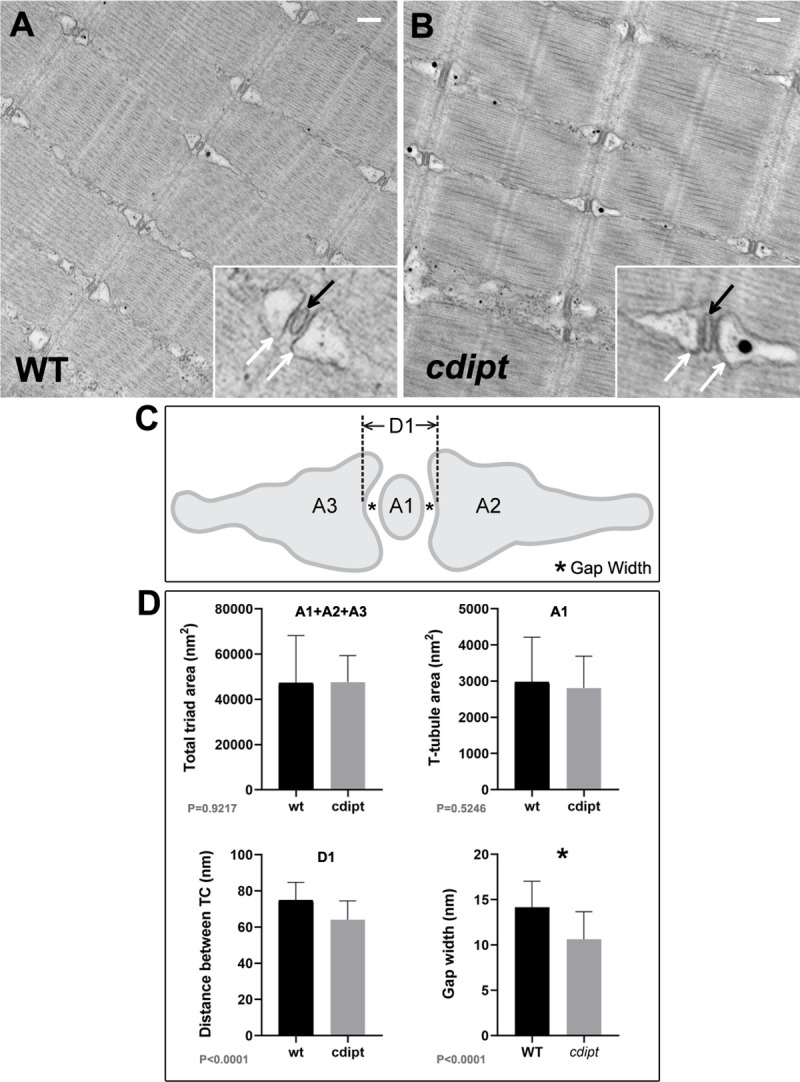
A-B) Transmission electron micrographs show normal skeletal muscle ultrastructure in cdipt larvae. T-tubules (insets; black arrow) are apposed by terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum (insets; white arrow). C) Diagram illustrating triad structure and features used for measurements: A1 = T-tubule area; A2 and A3 = terminal cisternae (TC) areas; D1 = maximum distance between TCs; * = gap width (distance between TC membrane and T-tubule membrane). D) There is no significant difference in the triad area between WT and cdipt mutant larvae (A1+A2+A3 graph) (n = 36, p = 0.9217). The T-tubule area (A1 graph) is qualitatively slightly smaller in the cdipt mutant than in WT (n = 36; P = 0.5246), whereas the distance between cisternae at maximum distance (D1 graph) (n = 36, p < 0.0001) and the gap width (* graph) (n = 44, p < 0.0001) are significantly smaller in cdipt mutants than in WT. Scale bars = 200 nm.
