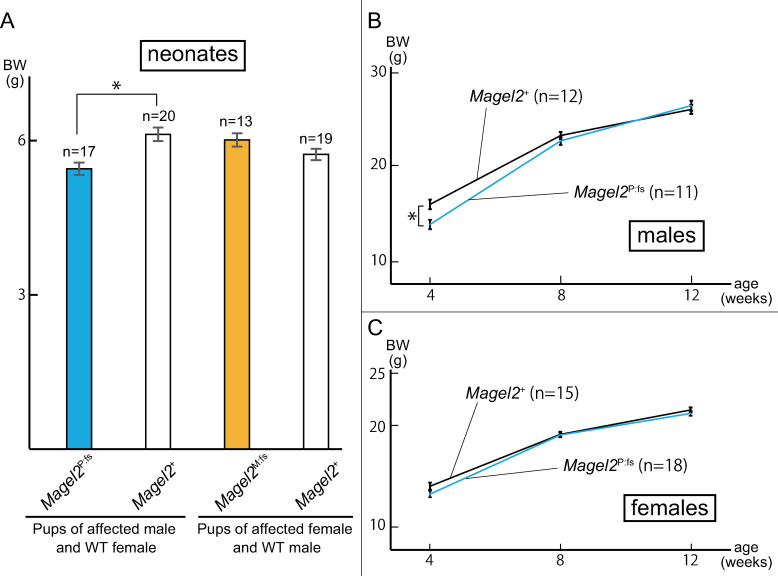
Fig 5. Comparison of body weight of affected and WT mice.
(A) Mean weight ± SEM at P10. The weight of Magel2P:fs was reduced compared to Magel2+ (5.44 ± 0.12 g vs 6.11 ± 0.13 g, P = 0.0003). There was no difference between Magel2M:fs and Magel2+ mice (6.00 ± 0.13 g vs 5.72 ± 0.11 g, P = 0.058). Both sexes were included. (B, C) Mean weight ± SEM at four, eight and 12 weeks of age in both sexes. At four weeks, Magel2P:fs males were lighter than Magel2+ (13.71 ± 0.49 g vs 15.84 ± 0.50 g, P = 0.0032), but by eight weeks of age, there was no difference. In females, there was no difference between Magel2P:fs mice and Magel2+ at four, eight and 12 weeks of age.