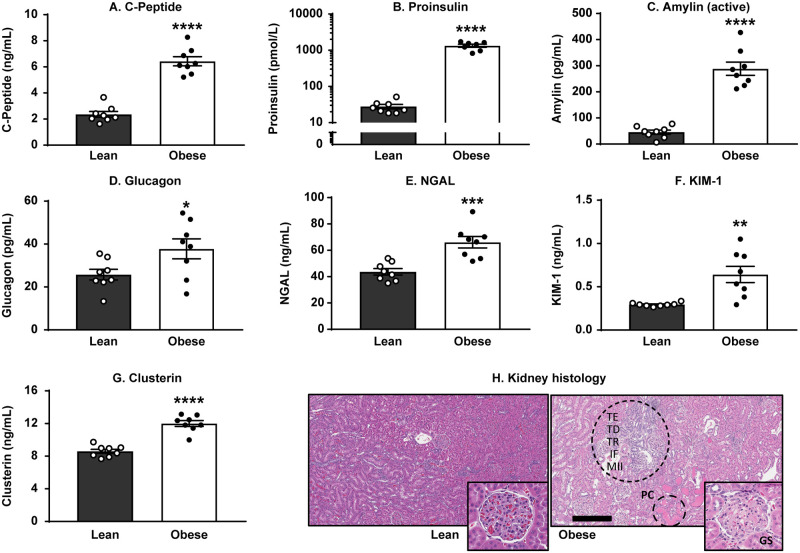
Fig 2. Obese ZSF1 rats demonstrated pancreatic dysfunction and impaired renal function.
Obese ZSF1 rats show increased C-peptide (A), proinsulin (B), active amylin (C), and glucagon (D). Obese ZSF1 rats exhibit impaired renal function by showing increased serum levels of kidney injury markers NGAL (E), KIM-1 (F), and clusterin (G). Stars (*) indicate significance (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001) by unpaired two-tailed t test. n = 8 for lean and n = 8 for obese ZSF1 groups. The following pathology was observed in obese ZSF1 kidneys (H): protein casts (PC), tubular ectasia (TE), tubular degeneration (TD) and regeneration (TR), minimal interstitial fibrosis (IF), infiltration by mononuclear inflammatory cells (MII), and minimal glomerulosclerosis. Bar = 300 μm.