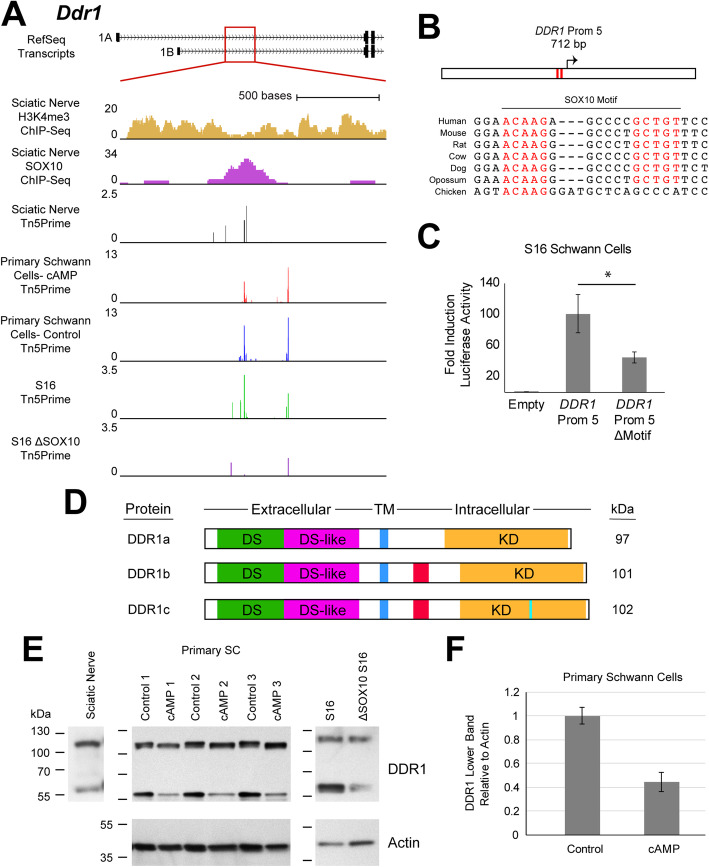
Fig. 7.
SOX10 regulates the expression of a novel Ddr1 transcription start site in Schwann cells. a The genomic locus at rat Ddr1 intron 1. Y-axes for H3K4me3 and SOX10 ChIP-Seq data: fold enrichment of sequencing reads above chromatin input. Y-axes for Tn5Prime data from rat sciatic nerve, CPT-cAMP- (cAMP) and vehicle-treated (Control) primary Schwann cells, and unmodified and ΔSOX10 S16 cells: number of transcript 5’ends mapped per base, in reads per million. b The 712-base pair DDR1 Prom 5 is shown along with the position of the SOX10 dimeric consensus sequence (red bars and red text). The seven species utilized for comparative sequence analysis are shown on the left. cDDR1 Prom 5 (with or without the dimeric SOX10 sequence, as indicated) was tested in luciferase reporter assays in cultured Schwann (S16) cells. Y-axis: fold induction of luciferase activity; error bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisk indicates p < 1 × 10− 4. d DDR1 isoforms a, b, and c contain discoidin (DS, green), discoidin-like (DS-like, magenta), transmembrane (TM, blue) and kinase (KD, orange) domains, and are distinguished by insertions in the intracellular sequences (red and light blue). Predicted molecular weights based on amino acid sequences are shown in kilodaltons (kDa) on the right. e DDR1 protein expression in sciatic nerve, primary Schwann cells, and S16 cells. Actin was used as a protein loading control. Numbered dashes to the left of each blot indicate the position of protein size markers in kilodaltons (kDa). f The intensity of the lower DDR1 band relative to Actin signal in control and cAMP-treated primary Schwann cells. The average across three independent samples is indicated by the bar height. Error bars indicate standard deviations