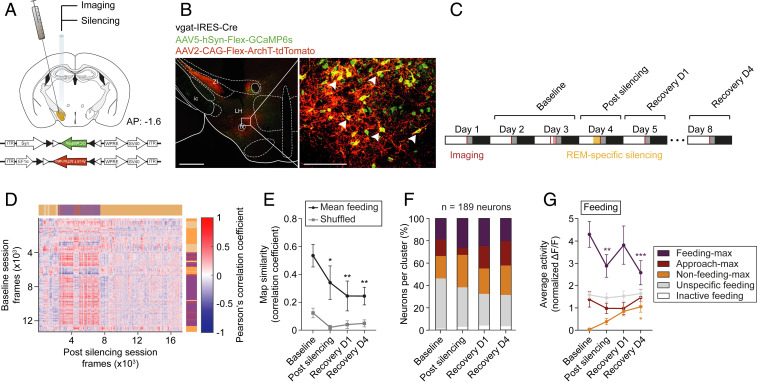
Fig. 6.
Optogenetic silencing of LHvgat neurons during REM sleep induces long-term changes in the feeding map. (A) Schematic of genetic cotargeting of GCaMP6s and ArchT-tdTomato to the LH of vgat-IRES-Cre mice for calcium imaging and optogenetic silencing, respectively. Animals were implanted with a GRIN lens for silencing and recording. The GCaMP6s and ArchT-tdTomato expression cassettes are shown on the bottom. (B) Photomicrograph of long-term cell-specific expression of GCaMP6s (green) and ArchT-tdTomato (red) in the LH from vgat-IRES-Cre mice (Left). Right shows enlargement of the white box highlighted in Left; the arrows show GCaMP6s/ArchT-tdTomato double-expressing LHvgat neurons. fx, fornix; ic, internal capsule; LH, lateral hypothalamus; ZI, zona incerta. (Scale bars: Left, 500 µm; Right, 100 µm.) (C) Timeline of optogenetic silencing and calcium recording, concomitant to EEG/EMG measurements for up to eight consecutive days. (D) Representative REM sleep population vector correlation matrix before (rows, vertical) and immediately after REM sleep-specific optogenetic silencing (columns, horizontal). Video-tracked and scored behaviors are indicated using color coding. Note that the matrix is not square because the sessions contain a different number of frames. (E) True average population vector similarity (black) and shuffled (gray) ± SEM between the feeding vectors across experimental timeline (n = 5 animals). Two-way RM ANOVA, FSession(3, 12) = 4.23, FShuffle(1, 4) = 10.38 with Dunnett’s post hoc test against baseline, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (F) Bar graph shows the classification of imaged neurons across experimental timeline (n = 5 animals). (G) Average activity ± SEM of the different functional clusters across the experimental timeline for feeding behavior. Two-way RM ANOVA, FCluster(3, 183) = 20.4, FCluster x Session(9, 549) = 3.28 with Dunnett’s post hoc test against baseline, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.