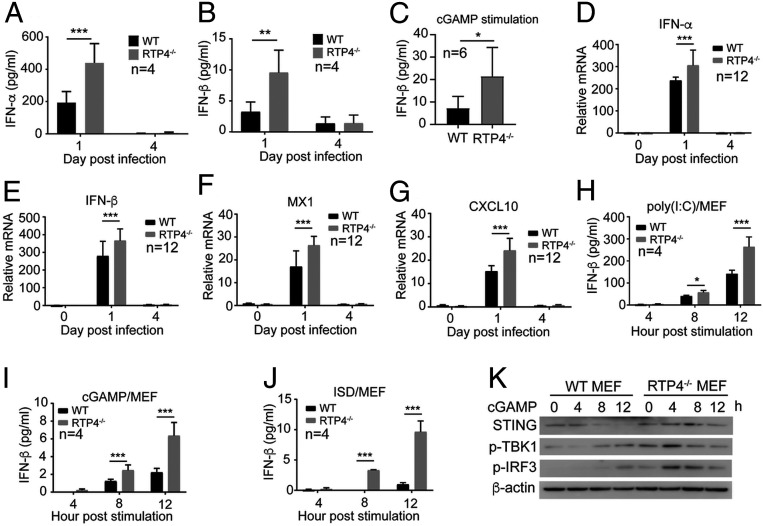
Fig. 6.
Disruption of Rtp4 gene in MEF cells and mice increases IFN-I responses. (A and B) Detection of IFN-α (A) and IFN-β (B) protein levels in the blood of Rtp4−/− and WT mice at days 1 and 4 p.i. with N67 parasites. (C) IFN-β levels in Rtp4−/− and WT mice at 6 h after i.v. injection of cGAMP (50 μg/mice). (D–G) mRNA levels for IFN-α (D), IFN-β (E), MX1 (F), and CXCL10 (G) in the spleens of Rtp4−/− and WT mice at days 0, 1, and 4 p.i. with N67 parasites. (H–J) IFN-β levels in culture media after stimulation of MEF cells with poly(I:C) (H), cGAMP (I), and ISD (J) for 4, 8, and 12 h. IFN-α and IFN-β from mouse blood and supernatants of MEF cultures were measured using ELISA kits (PBL Assay Science). mRNA levels were measured using qPCR as described in Materials and Methods. Means and SD from replicates (n) as indicated; two-way ANOVA: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (K) Western blot detection of STING protein expression and levels of TBK1 and IRF3 phosphorylation in Rtp4−/− and WT MEF cells after cGAMP stimulation. All experiments were independently repeated with similar results.