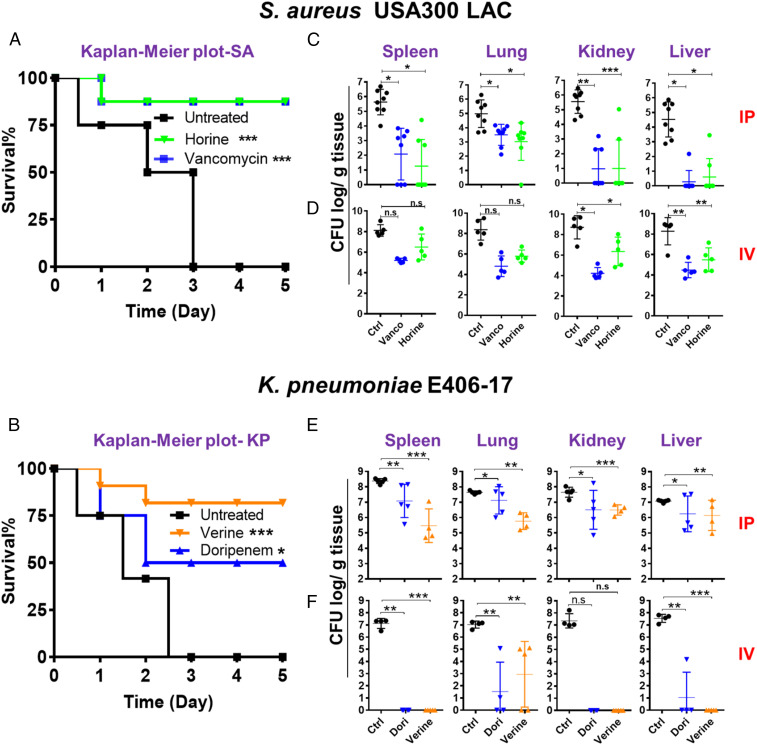
Fig. 5.
Systemic efficacy of horine and verine in neutropenic mice administered intraperitoneally (IP) or intravenously (IV). (A) Mouse survival after S. aureus USA300 LAC infection (∼2 × 107 CFU) without (black) and with a single dose treatment (intraperitoneally, 2 h postinfection) of horine (green) or vancomycin (vanco, blue) at 10 mg/kg. (B) Mouse survival after K. pneumoniae E406-17 infection (∼1 × 107 CFU) without (black) and with a single dose of verine (orange) and doripenem (dori, blue) at 15 mg/kg. Survival of the C57BL/6 mice (n = 8 in each group) was observed for 5 d postinfection. (C–F) The CFU burden in spleen, lung, kidney, and liver 24 h after infection of neutropenic mice treated with the peptide via either the intraperitoneally (C and E) or intravenously (D and F) route. (C and D) Mice were intraperitoneally infected with S. aureus USA300 LAC at 2 × 106 CFU per animal without (black) and with horine (green) or vancomycin (blue) treatment at 10 mg/kg 2 h postinfection (n = 8, C57BL/6 mice intraperitoneally, and n = 5, BALB/c mice intravenously). (E and F) Mice were intraperitoneally infected with K. pneumoniae E406-17 at 5 × 105 CFU per animal without (black) and with verine (orange) or doripenem (blue) treatment at 15 mg/kg 2 h postinfection, n = 5 (C57BL/6 mice intraperitoneally and BALB/c mice intravenously). The bacterial loads from each mouse were plotted as individual points and error bars represent the deviation within the experimental group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001 (determined by t test); n.s., not significant.