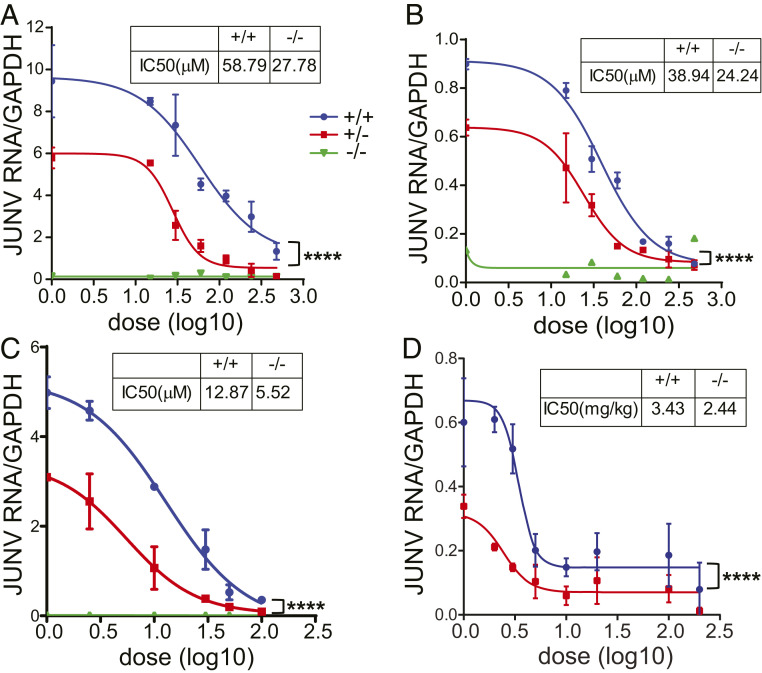
Fig. 6.
A1S +/− cells and mice are more resistant to JUNV-C1 infection and more susceptible to VGCC-targeting drugs. (A and B) MEFs (A) and SMs (B) were pretreated with increasing doses of GBP for 5 h, infected with JUNV-C1 for 1 h at 37° with GBP-supplemented medium, and incubated for another 40 h when JUNV-C1 RNA levels were analyzed. (C) MEFs were pretreated with increasing dosages of verapamil for 1 h and infected with JUNV-C1, as described for GBP treatment. (A–C) Shown are the averages of two independent experiments. (D) Eight- to 12-week-old A1S WT and +/− mice were treated with GBP by i.p. injection and, 1 h afterward, intracranially infected with JUNV-C1. GBP was administrated daily, and on day 5 postinfection, brains were harvested, and viral RNA was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Average values for each of the drug concentrations and numbers of mice at each drug concentration are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S6. Statistical significance of the curves was determined by two-way ANOVA. ****P ≤ 0.0001.