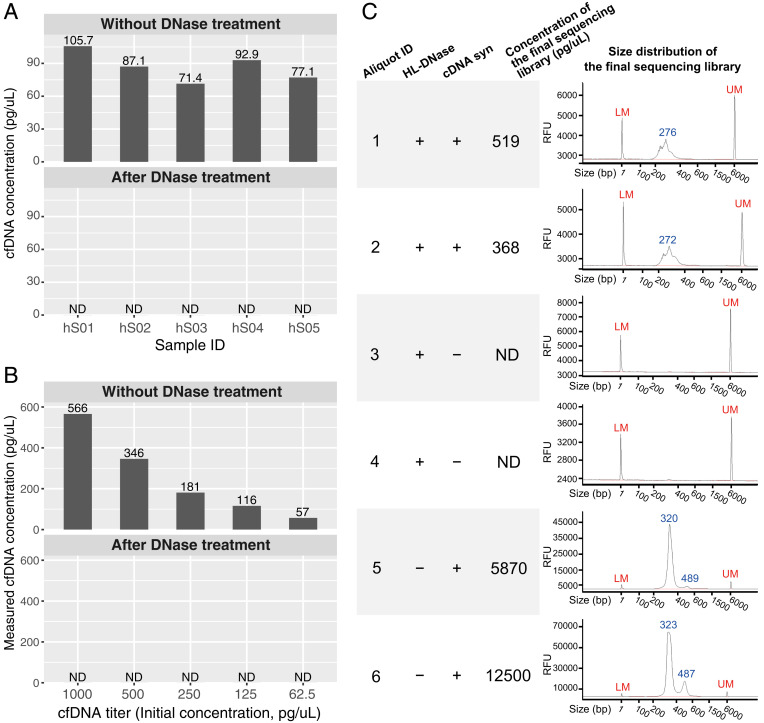
Fig. 1.
DNA contamination tests. (A) Concentrations of cfDNA in five human serum samples (IDs: hS01 to hS05, columns) before and after SILVER-seq’s DNase treatment step. Each serum sample (column) was split into two 7-µL aliquots which were subjected to no treatment (Upper) or DNase treatment (Lower). ND, not detectable. The detection limit of Qubit’s high-sensitivity kit is 0.5 pg/µL. (B) Measured concentrations of cfDNA titers (columns) before (Upper) and after (Lower) SILVER-seq’s DNase treatment step. The detection limit of Qubit’s high-sensitivity kit is 0.5 pg/µL. (C) Size distributions of six sequencing libraries from six aliquots of the same serum sample (aliquot ID: 1 to 6), with two aliquots (1 and 2) following the intact SILVER-seq protocol (HL-DNase: +, cDNA syn: +), two aliquots (4 and 5) following the complete protocol except the cDNA syn step (HL-DNase: +, cDNA syn: −), and two aliquots (5 and 6) following the complete protocol except the DNA digestion step (HL-DNase: −, cDNA syn: +). The concentrations of the sequencing libraries (fourth column) were reported by Qubit’s high-sensitivity kit. The size distributions (fifth column) were reported by Fragment Analyzer. RFU, relative fluorescence unit; LM, lower marker; UM, upper marker.