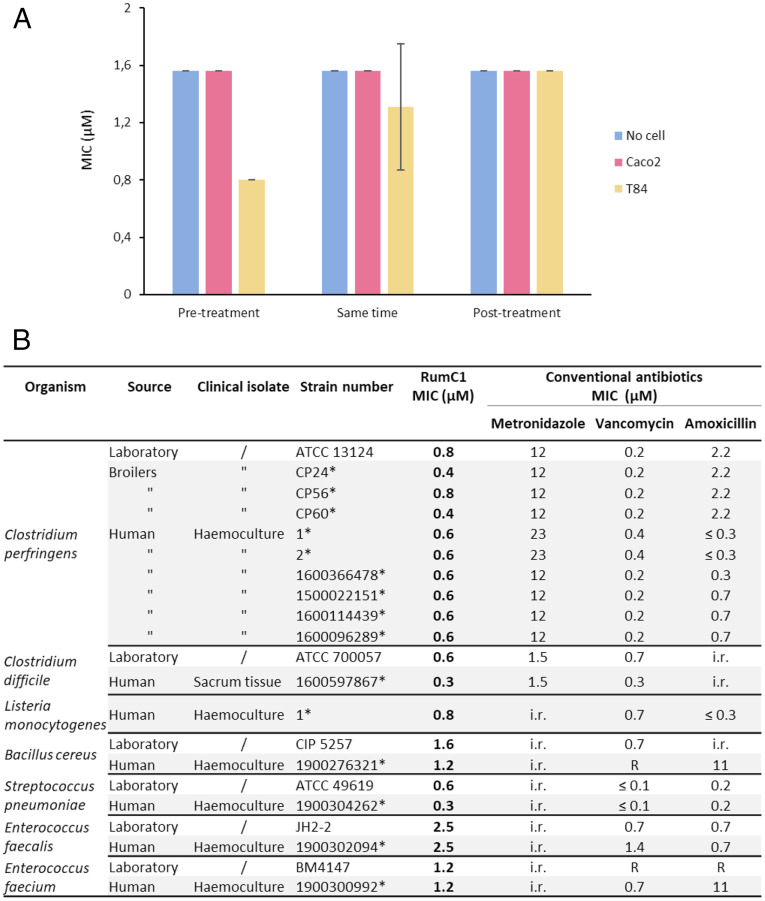
Fig. 4.
Antimicrobial activity of RumC1. (A) Activity assays of RumC1 on B. cereus grown in eukaryotic cell culture medium in the absence or the presence of a simulated intestinal epithelium. Small and colic intestine compartments were simulated by Caco2 and T84 culture cells monolayer respectively, whereas RumC1 was added before (30 min), concomitantly with, and after infection (30 min) with 5 × 105 CFU/mL B. cereus culture. (B) Activity spectrum of RumC1 against laboratory and clinical gram-positive pathogens. Collection strains and clinical isolates are indicated. The table includes MIC of conventional antibiotics commonly used for clinical treatment and considered here as references (i.e., metronidazole, vancomycin, and amoxicillin). Acquired resistance to antibiotics were determined following the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing 2019 clinical breakpoint tables and are indicated by R, whereas i.r. refers to intrinsic resistance, and asterisk refers to the laboratory isolate references.