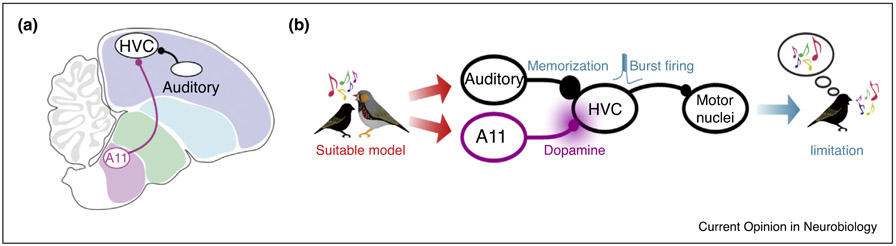
Figure 1.
Integration of social and auditory cues in the juvenile songbird’s brain. (a) A sagittal view of the songbird brain emphasizing the convergence in HVC of dopaminergic inputs (from the midbrain cell group A11) and auditory inputs from the sensorimotor nucleus NIf. (b) The juvenile’s encounter with a signing tutor triggers coincident activity of auditory and dopamine inputs to HVC, promoting song memorization, burst firing in the motor network, and song imitation. Reproduced from Tanaka et al. [62••].