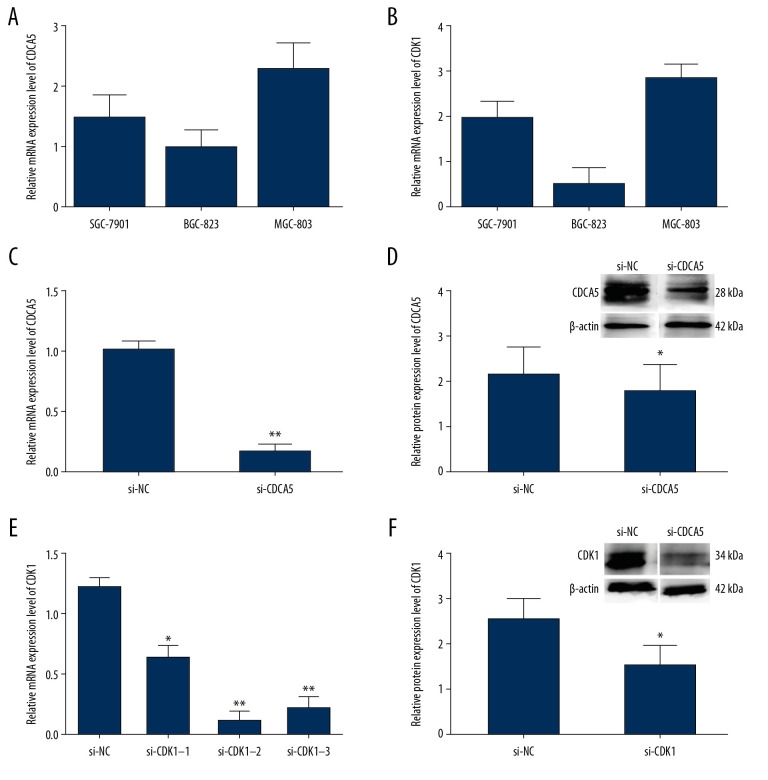
Figure 4.
The relationship of CDCA5 and CDK1 in MGC-803 cells. The relative CDCA5 mRNA levels (A) and CDK1 mRNA levels (B) were analyzed in 3 different GC cell lines SGC-7901, BGC-823 and MGC-803 using RT-qPCR. Among which, MGC-803 cells could effectively be expressed in both CDCA5 and CDK1, and thus was chosen as the research cell line in this study. (C) Cells were assigned for 2 groups and transfected with the control siRNA (si-NC) and si-CDCA5, respectively. The CDCA5 mRNA level was reduced significantly compared with the control group (** P<0.01). (D) The CDCA5 protein level was reduced significantly compared with the control (* P<0.05). The results suggested the si-CDCA5 fragment was effective. (E) Cells transfected with three different CDCA5-specific siRNAs were named as si-CDK1–1, si-CDK1–2 and si-CDK1–3, respectively. Group transfected with scramble siRNA was named as si-NC and worked as a control. Compared with the si-NC control group, the mRNA level of CDK1 in the 3 siRNA interfering groups were all reduced, among which, the si-CDK1–2 group reduced most significantly (* P<0.05 and ** P<0.01). Thus, we selected si-CDK1–2 as the specific siRNA fragment against CDK1 for the following experiments and renamed si-CDK1. (F) The protein expression levels of CDK1 in the si-CDK1 group and the control. Consistent with the result in (E), the protein expression level reduced significantly in the si-CDK1 group (* P<0.05).