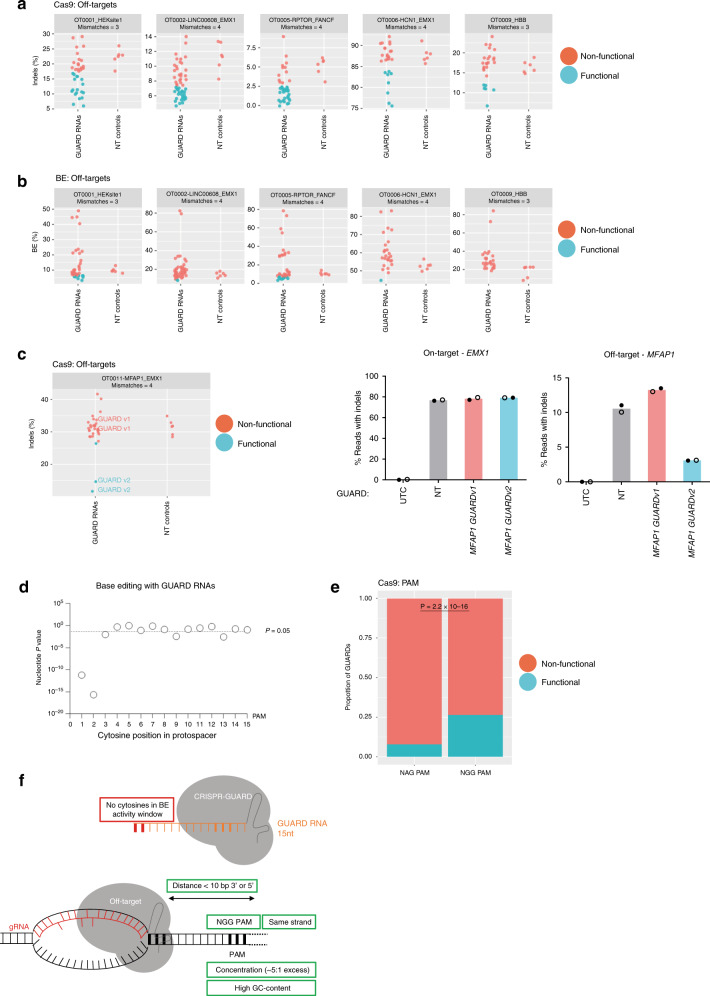
Fig. 6. GUARD RNA features that significantly reduce off-target editing.
a GUARD RNA performance for Cas9 and, (b) BE3. Base editing rates for BE (% of NGS reads with SNPs) or indel rates for Cas9 (% of NGS reads with indels) for a subset of off-target sites. Off-targets are labelled with an identifier, gene name (if genic), gRNA name, and the number of mismatches between the gRNA and the off-target site. Data are pooled from two independent experiments from cells treated with doxycycline. Each point represents a GUARD RNA and are compared to three non-targeting (NT) control RNAs. GUARD RNAs are classed as functional if they reduce off-target editing by at least two standard deviations from the mean of the NT controls. Data shown here is a subset of that presented in Supplementary Fig. 10. c Lentiviral plasmid screening reveals GUARD RNAs that are effective at endogenous genomic loci. (Left panel) indel rates from GUARD RNA screening of EMX1 gRNA off-target site MFAP1, highlighting non-functional GUARD RNA (v1) and functional GUARD RNA (v2). Screening data shown here is a subset of that presented in Supplementary Fig. 10. (Right panels) indel rates from amplicon sequencing of on-target and off-target endogenous loci from Cas9-expressing HEK293 cells transfected with EMX1 gRNA and GUARD RNA v1, GUARD RNA v2 or a NT control (all at 25 nM). Data represent mean of two independent experiments with symbols representing each replicate. d GUARD RNAs can mediate base editing at position 1 and 2 within the 15-nt GUARD RNA. GUARD RNAs were grouped according to whether they had a cytosine at each nucleotide position or not, and P values were generated by comparing the % of NGS reads with SNPs between GUARD RNA groups with an unpaired, two-tailed student’s t-tests. e Functional GUARD RNAs predominantly have NGG PAMs. The proportion of functional GUARD RNAs from the Cas9 screen that had NGG PAMs versus NAG PAMs was compared using a two-sided Fisher’s exact test. f Model depicting important parameters for GUARD RNA design. For GUARD RNAs that reduce Cas9 off-target editing, reducing distance from the gRNA, having an NGG PAM, binding to the same DNA strand as the gRNA, increased GC-content and high concentration in the cell will all increase the effectiveness of CRISPR GUARD. For BE3, the presence of cytosines at position 1 or 2 is to be avoided for 15-nt GUARD RNAs to prevent editing. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.