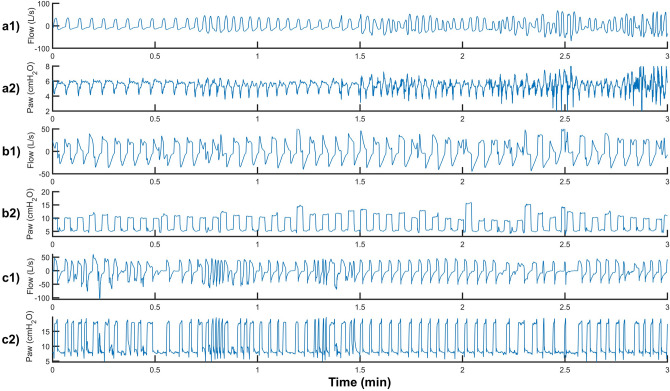
Figure 1.
Tracing of Flow and Paw from three different patients. (a) Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) of 6 cmH2O. (b) Pressure assist-control ventilation (PCV) with pressure of 10 cmH2O, (c) PSV with a pressure support of 10 cmH2O and PEEP of 8 cmH2O. In (a1) and (a2), Complex Patient-Ventilator Interactions (CP-VI) consists of an increase in respiratory rate > 50%; in (b1) and (b2), it consists of > 30% asynchronies (ineffective expiratory effort, double cycling, premature cycling, prolonged cycling, and/or reverse triggering) in the 3-min period; and in (c1) and (c2) it consists of a combination of change in the respiratory rate and asynchronies.