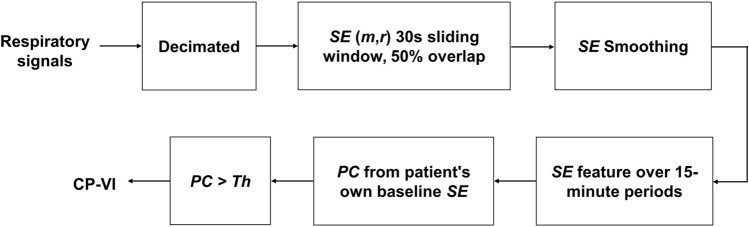
Figure 2.
Automatic CP-VI detection. Respiratory signals (Flow and Paw) are decimated at a sampling rate of 40 Hz. Sample entropy (SE) is calculated for different values of the embedding dimension (m) and tolerance (r). An 8-period-long exponential moving average is used to reduce noise and to increase the consistency of the SE results. Two SE features are determined for each 15-min period: the mean value and the maximum value. The percentage of change (PC) from the patient's own baseline value is calculated for each SE setting. When PC exceeds a determined threshold (Th), the period is considered to contain a CP-VI event. An optimization procedure is required to select the values of m, r, Th, respiratory signal, and SE feature that yield the most robust estimations of CP-VI.