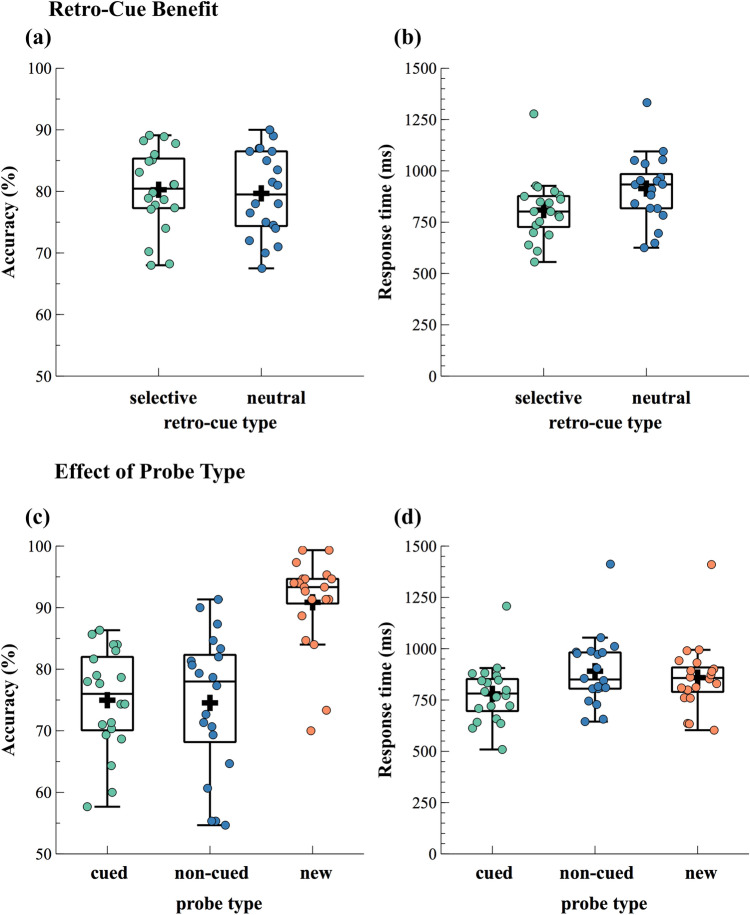
Figure 3.
Accuracy (a,c) and response times (b,d), depending on the comparisons considered for statistical analyses. To test for benefits of selective retro-cues, performance in selective and neutral retro-cues was compared, using paired sample t-tests. Because in neutral retro-cue trials, it was not possible to probe a non-cued item, the data depicted for selective retro-cues do not include non-cued probe trials (a,b). Accuracy (c) and response times (d), depending on probe type, refer exclusively to selective retro-cue trials because neutral retro-cue trials did not allow for the main comparison of interest between non-cued and new items. A repeated-measured ANOVA was conducted to test for effects of probe type. For further details on statistical analyses see the methods section. Boxplots illustrate the interquartile range and the median. Whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range. The dots indicate individual participants’ mean scores per condition. A black cross denotes the mean values across subjects for each condition.