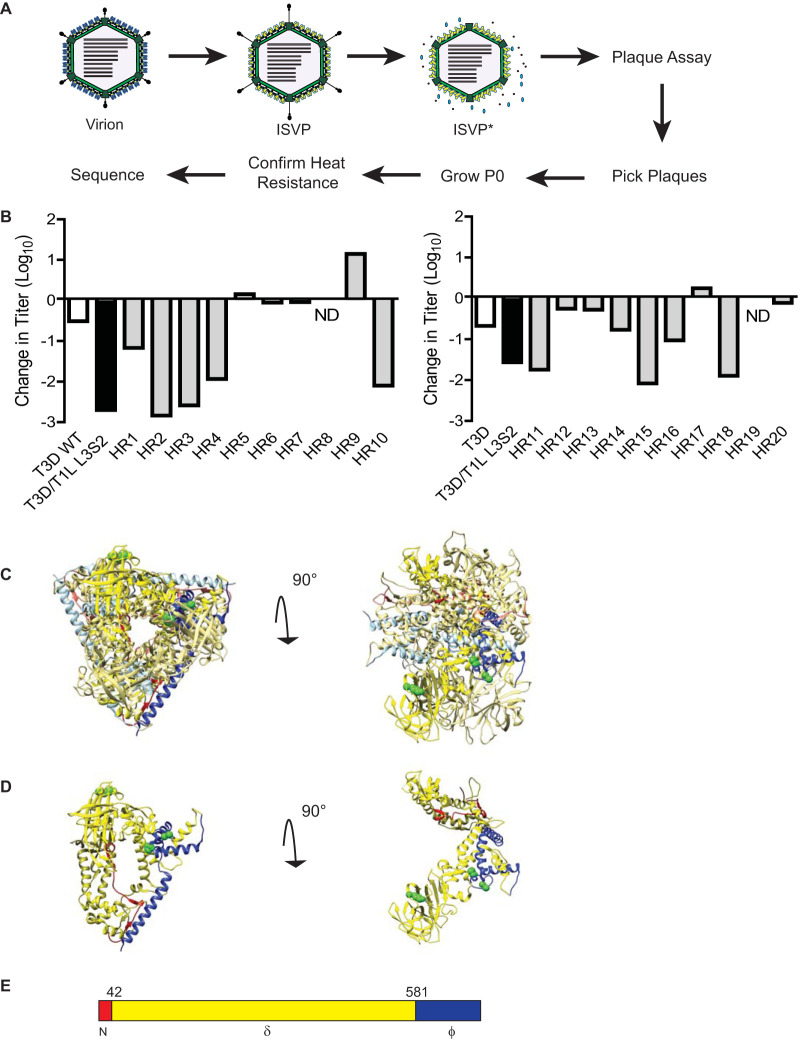
FIG 4.
Selection of viruses with mutations that confer stability to T3D/T1L L3S2 ISVPs. (A) Diagram depicting the process for selecting for mutants with reduced ISVP-ISVP* conversion efficiency of T3D/T1L L3S2. ISVPs of T3D/T1L L3S2 were incubated at 40°C for 20 min. Reaction mixtures were then diluted in PBS and subjected to plaque assay. Viruses from resulting plaques were isolated and propagated to generate P0 stocks. Heat resistance of these putative heat-resistant (HR) plaque isolates was confirmed by measuring the thermal stability of ISVPs incubated at 4°C or 40°C using a plaque assay. Mutants that were confirmed as heat resistant were sequenced. (B) ISVPs generated from P0 stocks were incubated at either 4°C or 40°C for 20 min. Reaction mixtures were then diluted in PBS and subjected to plaque assay. Note that HR1 to -10 and HR11 to -20 are from two separate isolation experiments, collected and tested at different times. ND, not detectable. (C and D) Top (left) and side (right) views of the μ1 trimer (C) and monomer (D). Positions of mutations identified in HR viruses are shown in green. μ1 cleavage fragments are colored as in panel E, with one μ1 monomer shown with darker colors.