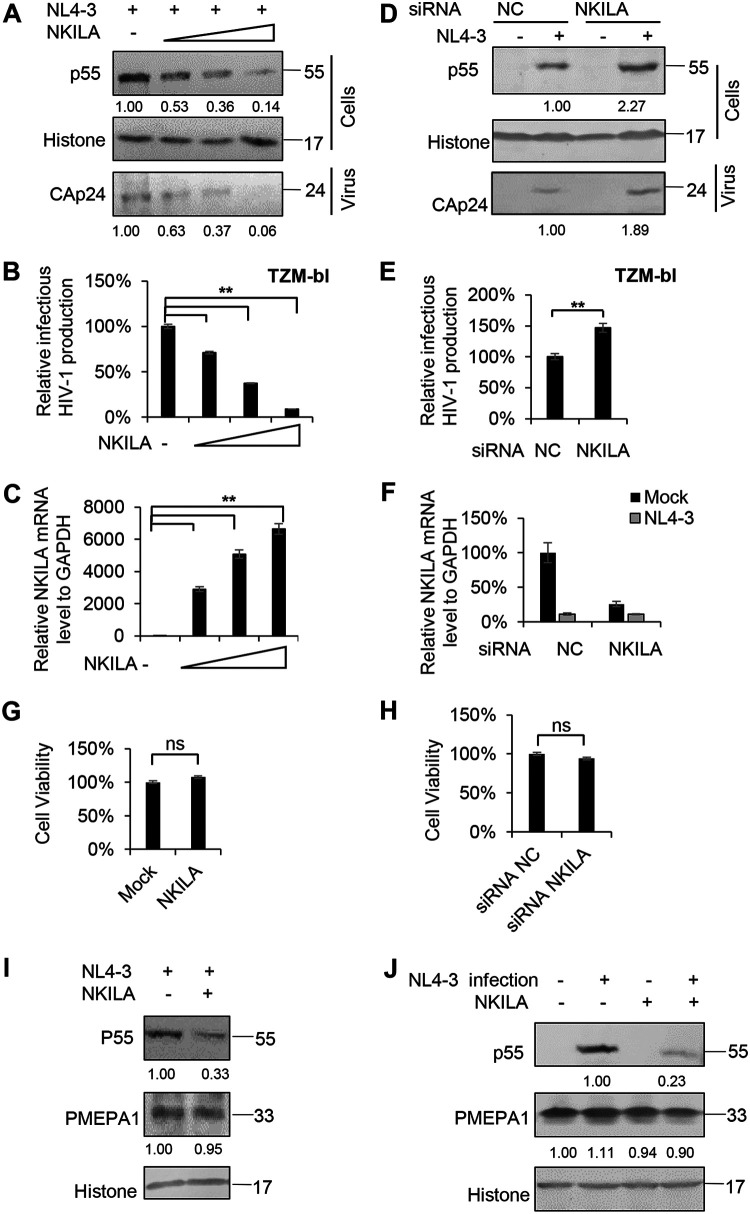
FIG 1.
NKILA inhibits HIV-1 replication. (A to C) Overexpression of NKILA inhibits HIV-1 replication in a dose-dependent manner. (A) Multiple dose amounts of NKILA expression vector (100 ng, 300 ng, and 900 ng) or negative-control vector were transfected with the pNL4-3 viral expression vector into HEK293T cells. After 48 h, cells and supernatants were harvested and analyzed by immunoblot (IB) analysis. The densities of bands from representative immunoblotting (IB) analyses were analyzed with ImageJ software to calculate the values, for cells relative to that for histone. (B) Infectious HIV-1 production was decreased with increasing NKILA expression, as indicated in TZM-bl cells. (C) The expression levels of NKILA mRNA were measured by qRT-PCR. The mRNA level of endogenous NKILA was set as 100%. (D to F) Knockdown of NKILA increased HIV-1 replication. (D) pNL4-3 or negative-control vector was cotransfected with siRNA NKILA or siRNA NC into HEK293T cells for 48 h. Cells and supernatants were harvested for IB analysis, and the densities of bands from representative IB analyses were analyzed as described for panel A. (E) NKILA increased the infectious HIV-1 production, as indicated in TZM-bl cells. The infectious HIV-1 production of siRNA NC was set as 100%. (F) The expression levels of NKILA in cells with NKILA knockdown were measured by qRT-PCR and normalized to GAPDH expression. Overexpression (G) or knockdown (H) of NKILA had no effect on cell viability by CCK-8 detection. (I)The inhibitory effect of NKILA on HIV-1 production was not associated with altered endogenous expression of the PMEPA1 protein. NKILA or negative-control vector was cotransfected with the pNL4-3 viral vector into HEK293T cells. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cell extracts were harvested and subjected to IB analysis with anti-PMEPA1 antibody to detect the PMEPA1 protein. (J) PMEPA1 protein expression was not affected by HIV-1 infection or NKILA expression. NKILA or negative-control vector was nucleofected to Jurkat cells. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, the cells were infected with the supernatant containing NL4-3 viral particles or an equal amount of medium. After 48 h of infection, cells were harvested for IB analysis. The densities of bands were analyzed as described for panel A. All results are presented as the means ± SDs from three independent experiments. ns, not significant; **, P < 0.01.