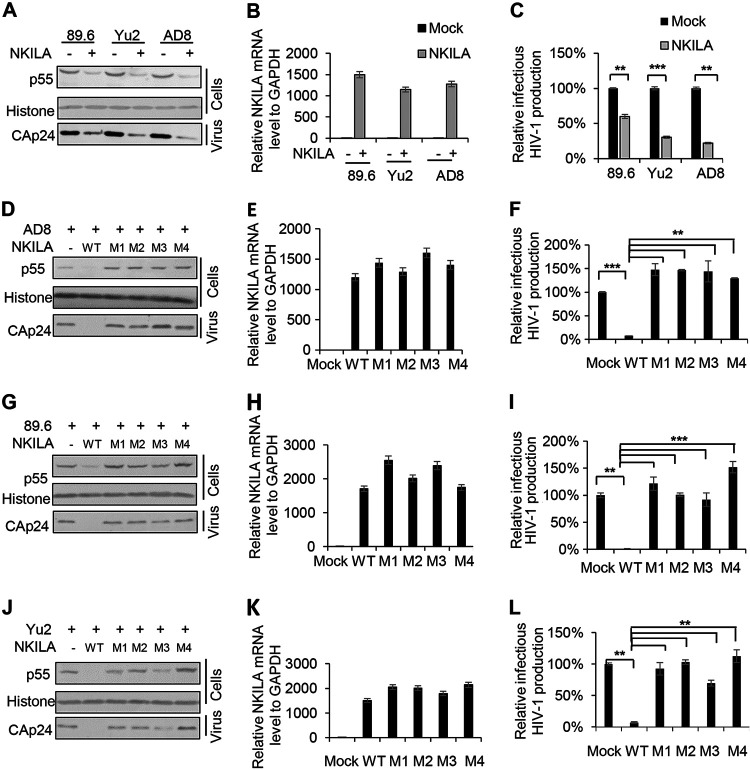
FIG 7.
NKILA has the ability to inhibit the replication of HIV-1 clones with different coreceptor tropisms. (A) Overexpression of NKILA suppressed the replication of HIV-1 clones with different coreceptor tropisms. The NKILA or negative-control vector was cotransfected with expression plasmids for the HIV-1 clones 89.6, Yu2, or AD8. Forty-eight hours posttransfection, cells and supernatants were harvested for measurement of HIV-1 gene expression by IB analysis (A) and were analyzed by qRT-PCR to measure NKILA mRNA levels (B). (C) TZM-bl cells were infected with viral supernatants for 48 h and harvested for measurement of infectious HIV-1 yield by a luciferase assay. (D to L) NKILA mutants lost their inhibition ability toward various HIV-1 clones. NKILA WT or the indicated mutants were cotransfected with expression vectors for the HIV-1 clones AD8 (D, E, and F), 89.6 (G, H, and I), or Yu2 (J, K, and L). Cells were harvested for detection of HIV-1 gene expression by IB analysis (D, G, and J) and were analyzed by qRT-PCR to measure NKILA mRNA levels (E, H, and K). Supernatants were used to infect TZM-bl cells for measurement of the infectious yield of various HIV-1 clones (F, I, and L). The corresponding value of the control was set as 1 or 100% as appropriate. All results are representative of three independent experiments. The data are presented as the means ± SDs. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.