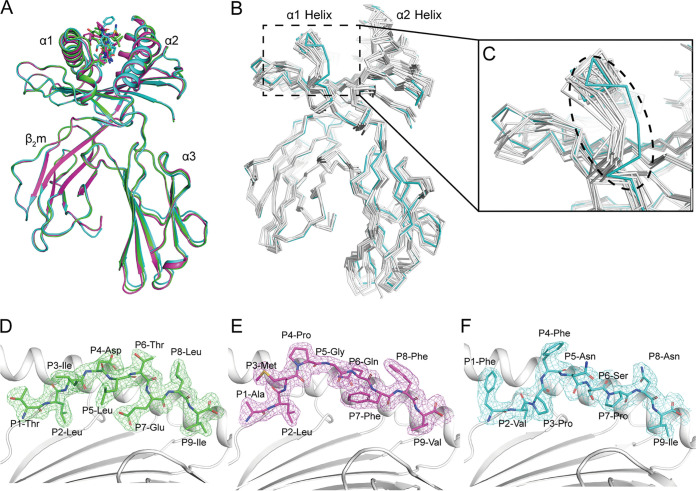
FIG 2.
Overall RLA-A1/peptide structures. (A) Structural alignment of RLA-A1/VP60-2 (magenta) and RLA-A1/VP60-10 (cyan) with RLA-A1/VP60-1 (green). The heavy chain of RLA-A1 and human β2m are shown as cartoons. Peptides are shown as sticks. (B) The superimposition of RLA-A1 (cyan) with other mammalian MHC-I molecules: human HLA-A*0201 (PDB code 3MGT), macaque Mamu-A*01 (PDB code 1ZVS), equine Eqca-N*00601 (PDB code 4ZUW), canine DLA-88*50801 (PDB code 5F1I), murine H2-Kd (PDB code 5GR7), feline FLA-E*01801 (PDB code 5XMF), swine SLA-1*0401 (PDB code 3QQ4), and bovine N*01801 (PDB code 3PWV) (all in white). (C) The main differences between RLA-A1 and other mammalian MHC-I molecules are located at the N terminus of the PBG, which is circled by a black dashed line. The authentic conformations of peptides VP60-1 (green) (D), VP60-2 (magenta) (E), and VP60-10 (cyan) (F) in the RLA-A1 PBG are shown in the 2Fo − Fc (where Fo and Fc are the observed and calculated structure factor amplitudes, respectively) electron groove density maps contoured at 1.0 s.