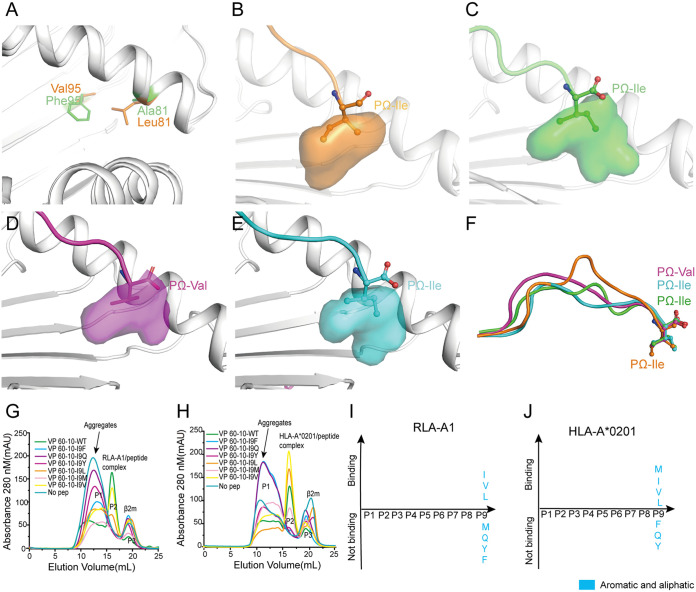
FIG 5.
The hydrophobic F pocket of RLA-A1 with a different orientation. (A) The structure comparison of key discrepant residues of the F pocket, 81 and 95, between RLA-A1 (green) and HLA-A*0201 (orange). The residues are shown as sticks. (B) The F pocket of HLA-A*0201 is shown as an orange cavity. PΩ-Ile of the peptide is shown as orange sticks and spheres. The backbone of HLA-A*0201 is shown as a cartoon in white. The F pocket of RLA-A1/VP60-1 is shown in green (C), RLA-A1/VP60-2 is shown in magenta (D), and RLA-A1/VP60-10 is shown in cyan (E). PΩ-Ile residues of VP60-1, VP 60-2, and VP60-10 are shown as green, magenta, and cyan sticks and spheres, respectively. The backbone of RLA-A1 is shown as a cartoon in white. (F) The comparison of peptides presented by HLA-A*0201 and RLA-A1. H5-HA205-214 presented by HLA-A*0201 (PDB code 3MGT) is shown in orange. VP60-1, VP60-2, and VP60-10 presented by RLA-A1 are shown in green, magenta, and cyan, respectively. PΩ residues of VP60-1, VP60-2, VP60-10, and H5-HA205-214 are shown as sticks and spheres. The binding motifs of the F pocket of RLA-A1 (G) and HLA-A*0201 (H) were evaluated through a series of substitution mutations at the PΩ position. According to the results of renaturation in vitro, RLA-A1 bound to peptides with small and aliphatic amino acids (Leu, Ile, and Val) (I) at the PΩ position, and HLA-A*0201 bound to peptides with amino acids Met, Leu, Ile, and Val (J) at this position.