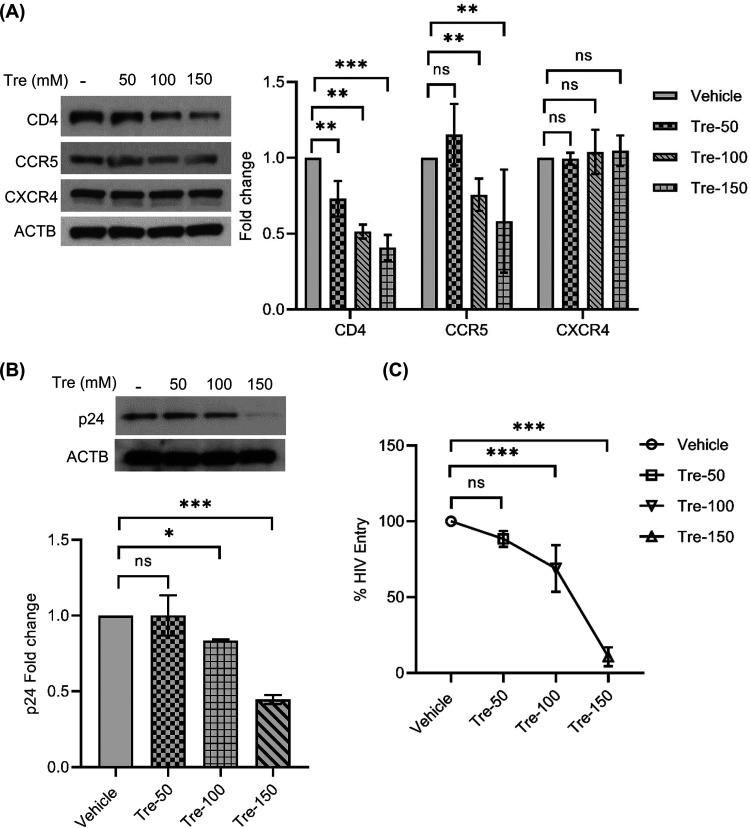
FIG 8.
Trehalose treatment inhibits HIV entry into human CD4+ T cells by modulating the CD4 and CCR5 expression. (A) PHA-T cells were treated with vehicle or trehalose (50 to 150 mM) for 6 h and analyzed for expression of CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4 by immunoblotting. (Left) Representative immunoblot showing the expression of CD4, CCR5, CXCR4, and ACTB. (Right) Relative fold change (densitometric analysis) in CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4 protein normalized to ACTB. (B and C) Untreated and trehalose-pretreated (73) T cells were exposed to HIV (0.04 MOI) for 8 h. At 24 p.i., cell lysates were prepared to detect HIV antigen by immunoblotting (B) and ELISA (C). Data are derived from four independent donors and presented as means ± s.e.m. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.