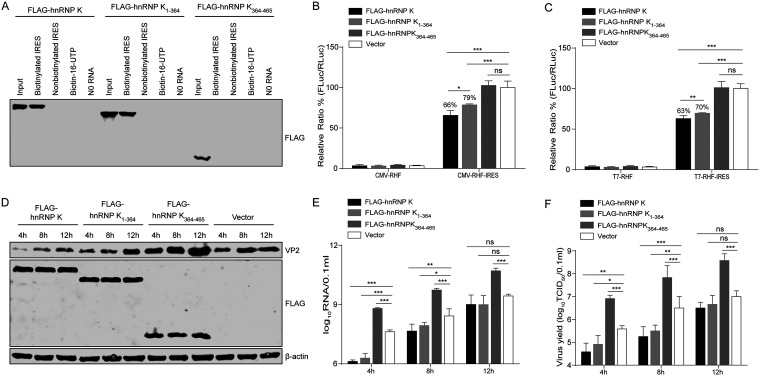
FIG 9.
Effect of hnRNP K products cleaved by 3C protease on IRES activity and FMDV replication. (A) Binding assay of hnRNP K and its truncated forms with FMDV IRES RNA. Lysates from HEK293T cells overexpressing FLAG-hnRNP K, FLAG-hnRNP K1–364, or FLAG-hnRNP K364–465 were purified by an anti-FLAG G1 affinity resin and incubated with biotinylated or nonbiotinylated FMDV IRES RNA, biotin-16-UTP, or no RNA. The protein-RNA complexes were pulled down with streptavidin beads and separated by SDS-PAGE. FLAG-tagged hnRNP K was detected by Western blotting. (B and C) Effects of hnRNP K and its truncated forms on FMDV IRES activity in vitro. BHK-21 cells were first transfected with FLAG-hnRNP K, FLAG-hnRNP K1–364, FLAG-hnRNP K364–465, or the FLAG vector control. After 24 h, the plasmid (pCMV-RHF or pCMV-RHF-IRES) (B) and the in vitro-transcribed RNA (T7-RHF or T7-RHF-IRES) (C) were transfected into BHK-21 cells. At 48 h posttransfection, the RLuc and FLuc activities in the cell lysates were analyzed. The luciferase activity of the FLAG vector control was set as 100%. (D to F) Effect of hnRNP K and its cleavage products (hnRNP K1–364 and hnRNP K364–465) on viral replication. BHK-21 cells were transfected with FLAG-hnRNP K, FLAG-hnRNP K1–364, FLAG-hnRNP K364–465, or the FLAG vector control and then infected with FMDV at an MOI of 1 at 24 h posttransfection. The cells and supernatants were harvested at 4, 8, and 12 hpi. (D) The full-length hnRNP K and hnRNP K truncations and viral VP2 levels in the cells were detected by Western blotting using anti-VP2, anti-FLAG, and antiactin antibodies, respectively. (E) The viral RNA levels in the cells were detected by RT-qPCR. (F) The viral titers in the supernatants were determined by TCID50 assays. (B, C, E, F) The results are presented as the means ± SD from at least three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate significant differences between groups, as assessed by Student's t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).