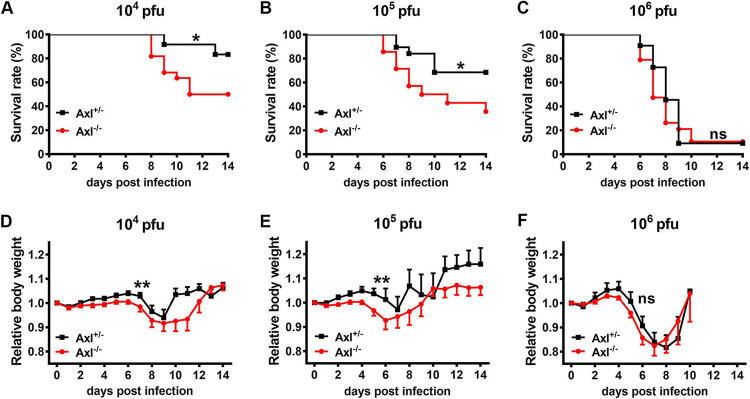
FIG 1.
Effects of Axl on Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection. Four-week-old Axl−/− and Axl+/− mice received an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of different doses of JEV (104, 105, and 106 PFU). (A to C) Survival curves of Axl+/− and Axl−/− mice infected with 104 PFU (A) (n = 12 for Axl+/−, n = 22 for Axl−/−), 105 PFU (B) (n = 19 for Axl+/−, n = 14 for Axl−/−), and 106 PFU of JEV (C) (n = 11 for Axl+/−, n = 19 for Axl−/−). The survival curves were compared by log-rank test. (D to F) Body weight changes of Axl+/− and Axl−/− mice infected with 104 PFU (D) (n = 26 for Axl+/−, n = 19 for Axl−/−), 105 PFU (E) (n = 7 for Axl+/−, n = 9 for Axl−/−), and 106 PFU of JEV (F) (n = 11 for Axl+/−, n = 19 for Axl−/−). The body weight changes were compared by two-way ANOVA. Data are expressed as means ± SEM; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ns, no significance (P > 0.05); each result is the representative of three independent experiments.