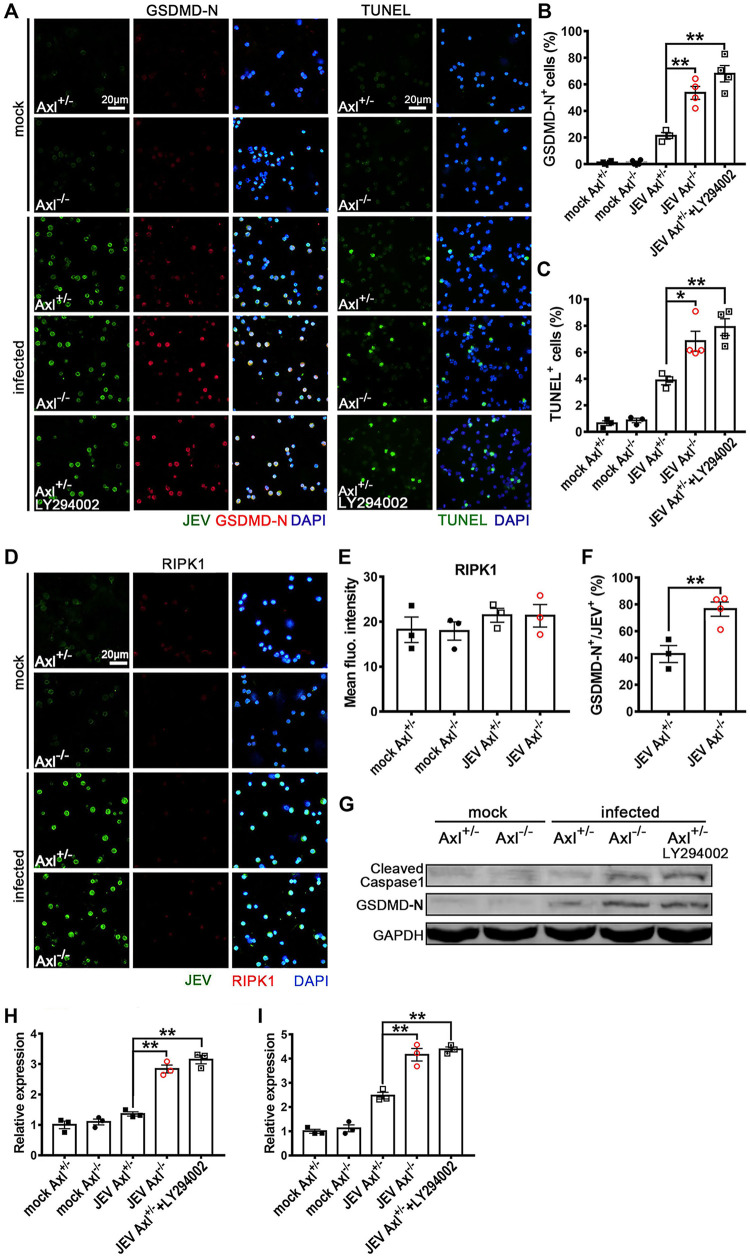
FIG 12.
Effect of Axl on the cell death mode of in situ peritoneal macrophages. Four-week-old Axl−/− and Axl+/− mice received an i.p. injection of 104 PFU of JEV. Specifically, for PI3K inhibition in the in situ Axl+/− peritoneal macrophages, an i.p. injection of LY294002 (1.25 mg per mouse) was administered 1 h prior to i.p. infection. At 24 hpi, the in situ peritoneal macrophages were isolated. (A) IF staining of GSDMD-N (marker of pyroptosis) and TUNEL staining (marker of apoptosis) of the in situ peritoneal macrophages. (B) Pyroptosis (GSDMD-N+) rates of the in situ peritoneal macrophages; n = 3 to 4 for each group; the data were compared by unpaired t test. (C) Apoptosis (TUNEL+) rates of the in situ peritoneal macrophages; n = 3 to 4 for each group; the data were compared by unpaired t test. (D) IF staining of RIPK1 (marker of necroptosis) in the in situ peritoneal macrophages. (E) Quantification of the fluorescence intensity of RIPK1 in the in situ peritoneal macrophages; n = 3 for each group; the data were compared by unpaired t test. (F) Pyroptosis (GSDMD-N+) rate of JEV-infected (JEV+) in situ peritoneal macrophages; n = 3 to 4 for each group; the data were compared by unpaired t test. (G) Immunoblotting detection of cleaved caspase-1 and GSDMD-N in the in situ peritoneal macrophages at 24 hpi. GAPDH was used as a loading control; n = 3. (H and I) Quantification of the gray density of cleaved caspase-1 (H) and GSDMD-N (I), normalized to the average of mock-treated Axl+/- macrophages; n = 3 for each group; the data were compared by unpaired t test. All the data are expressed as the means ± SEM; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; each result is the representative of three independent experiments.