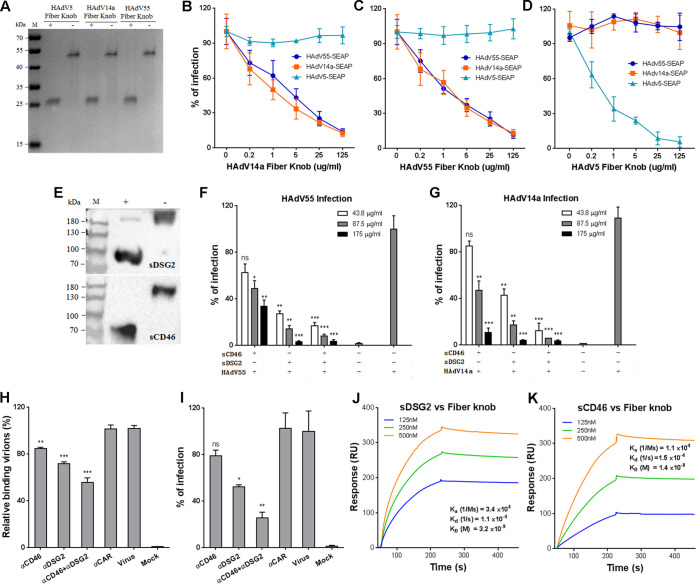
FIG 1.
Blocking the interaction of HAdV55 fiber with hDSG2 reduces HAdV55 binding and infection. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of the fiber knobs of HAdV5, HAdV14a and HAdV55. +, the samples were preheated in the presence of β-mercaptoethanol; -, the samples were not preheated and β-mercaptoethanol was not added. (B) HAdV14a fiber knob competitively inhibits the infection of HAdV55 and HAdV14a. (C) HAdV55 fiber knob competitively inhibits the infection of HAdV55 and HAdV14a. (D) HAdV5 fiber knob competitively inhibits the infection of HAdV5 but not HAdV55 or HAdV14a. A549 cells were preincubated with the fiber knob of HAdV14a, HAdV55, or HAdV5 and then infected with HAdV14a-SEAP, HAdV55-SEAP, or HAdV5-SEAP at 200 vp/cell. At 24 h postinfection, the SEAP activity in the cultured media was measured. Percent infection was calculated as the percentage of SEAP activity in fiber knob-treated cells versus that in PBS-treated cells. (E) Western blot analysis of sCD46 and sDSG2 under reducing and nonreducing conditions. (F) sDSG2 and sCD46 competitively inhibit HAdV55 infection. (G) sDSG2 and sCD46 competitively inhibit HAdV14a infection. HAdV55-SEAP or HAdV14a-SEAP was incubated with sDSG2, sCD46, or both and then used to infect A549 cells (200 vp/cell). At 24 h postinfection, the SEAP activity in the cultured media was measured. Percent infection was calculated as the percentage of SEAP activity resulting from HAdV55-SEAP or HAdV14a-SEAP infection in the presence of sDSG2, sCD46, or both versus that in the absence of these competitors. (H) hDSG2 antibodies reduce HAdV55 binding to host cells. A549 cells were preincubated with hDSG2 antibodies (6D8 and 8E5), hCD46 antibodies (M177 and MEM258), or both and then incubated with HAdV55. The relative bound viruses were measured by qPCR and calculated using β-actin as a reference. Genome copies of HAdV55 bound to A549 cells were taken as 100%. (I) hDSG2 antibodies reduce HAdV55 infection. A549 cells preincubated with either hDSG2 antibodies or hCD46 antibodies were infected with HAdV55-SEAP at 50 vp/cell. At 24 h postinfection, the SEAP activity in the cultured media was measured. Percent infection was calculated as the percentage of SEAP activity resulting from HAdV55-SEAP infection in the presence of anti-hDSG2 antibodies, anti-sCD46 antibodies, or both versus that in the absence of these antibodies. (J) Kinetics of binding of HAdV55 fiber knob to sDSG2. (K) Kinetics of binding of HAdV55 fiber knob to sCD46. Data are representative of those from three independent experiments and presented as the means ± standard deviations (SD). Comparison between groups was performed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA; n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significance.