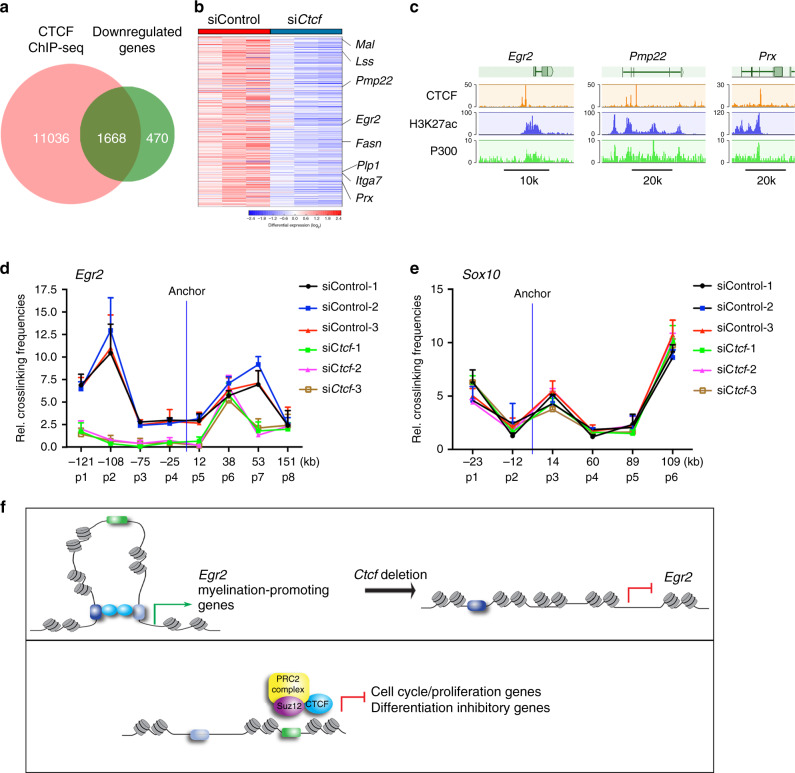
Fig. 10. CTCF-mediated chromatin regulatory looping is necessary for EGR2 expression.
a Venn diagrams depicting overlap between CTCF-bound genes and downregulated genes differentially expressed in rat SCs treated with control siRNA or siCtcf. b Heatmap of CTCF-targeted genes differentially downregulated in SCs treated with siCtcf compared to controls. n = 3 in each condition. c Genome browser tracks over the loci of selected myelin-related genes with ChIP-seq density mapping of CTCF, H3K27ac, and P300 from rat SCs. n = 1 in each condition with 20 million cells. d Quantitation of relative interaction frequencies between the indicated anchor site and neighboring Egr2 genomic restriction fragments. n = 3 independent 3C experiments. e Quantitation of relative interaction frequencies between the indicated anchor site and neighboring Sox10 genomic restriction fragments. n = 3 independent 3C experiments. f A model depicting a dual mode of action by CTCF in promotion of SC differentiation: CTCF stabilizes chromatin loops involving promotor-enhancer interactions to activate expression of promyelinating genes such as Egr2 (left panel) and forms a transcriptional co-repressor complex with SUZ12-PRC2 (right panel) to inhibit expression of genes such as Sox2 that encode factors that inhibit differentiation and cell-cycle/proliferation regulators. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.