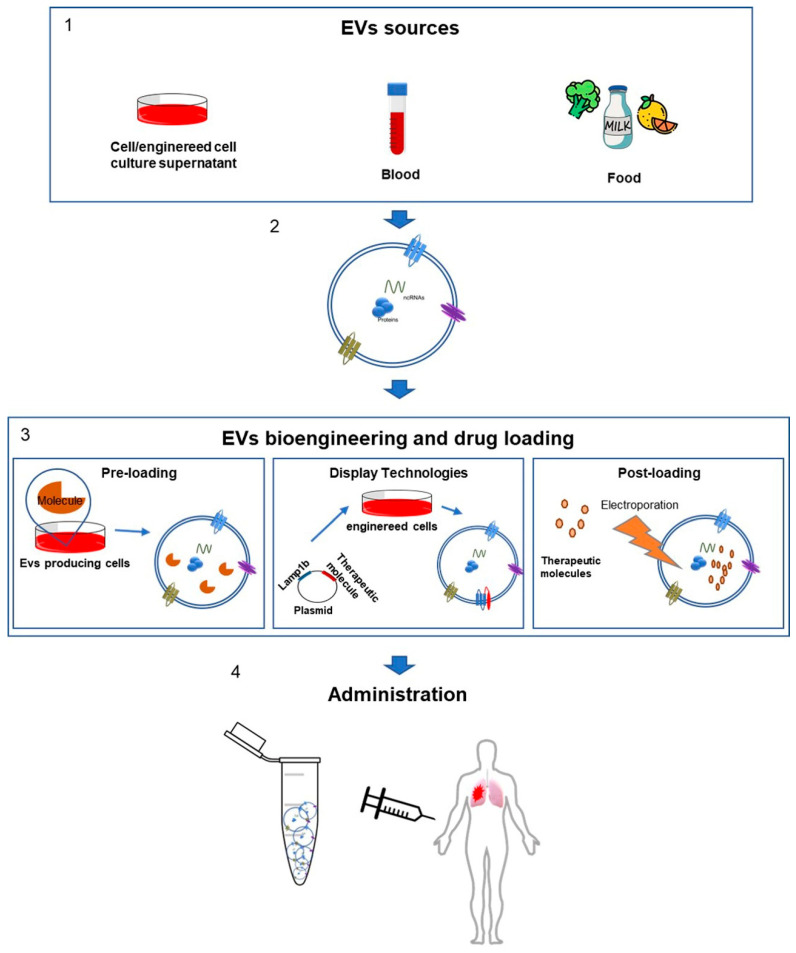
Figure 1.
Strategy of EVs modification for therapeutic purposes. The figure schematizes the approaches currently used in EVs engineering or in the manipulation of their content. (1) The EVs are promising candidates in the treatment of numerous pathologies and there are various reliable sources. EVs can be isolated from the cell culture supernatant of various producing cell lines, from body fluids and also from food. (2) The EVs molecular composition is complex and it depends on the cellular source. They can contain different classes of proteins (membrane-bound tetraspanins CD9, CD81 and CD63; receptors, heat shock proteins), ncRNAs (RNAs; MicroRNAs) and lipids (lysobisphosphatidic acid; phosphatidylcholine; phosphatidylethanolamine and sphingomyelin). (3) The different methods to manipulate the EVs content include the preloading approach, in which a pre-existing endogenous cargo is the therapeutic molecule. In the display technology, the EV-producing cells can be engineered with a plasmid in order to induce the expression of exogenous proteins. The post-loading method consists in the direct introduction of drug molecules into EVs after their isolation. (4) The engineered EVs may also be manipulated to be more bioactive and bioavailable and can be administered to patients for the MPM therapy.