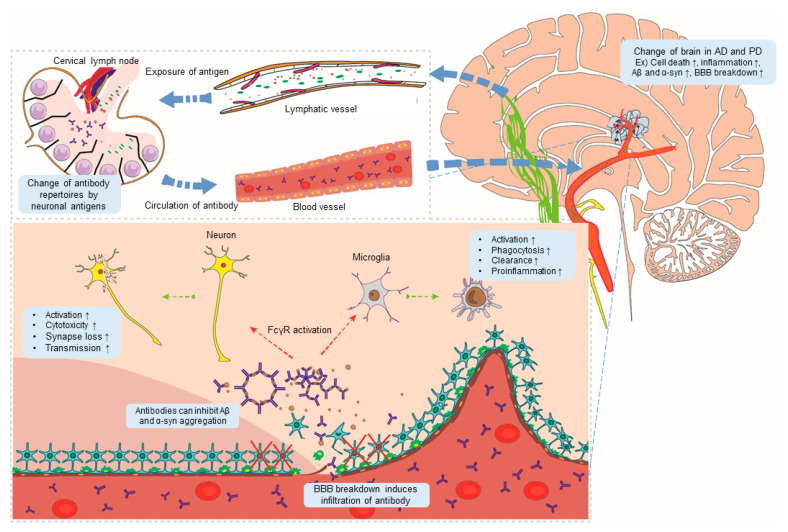
Figure 1.
A model showing antibody-mediated pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Changes in brain conditions in AD and PD (for example, cell death, inflammation, and aggregation of abnormal proteins) promote the outflow of neo-antigens through lymphatic vessels, causing changes in antibody repertoires. Damage to the blood–brain barrier (BBB) generated in AD and PD induces infiltration by antibodies. Antibodies activate FcR expression by brain cells, thereby promoting pathogenesis of AD and PD in the brain. Aβ: beta-amyloid; α-syn: α-synuclein.