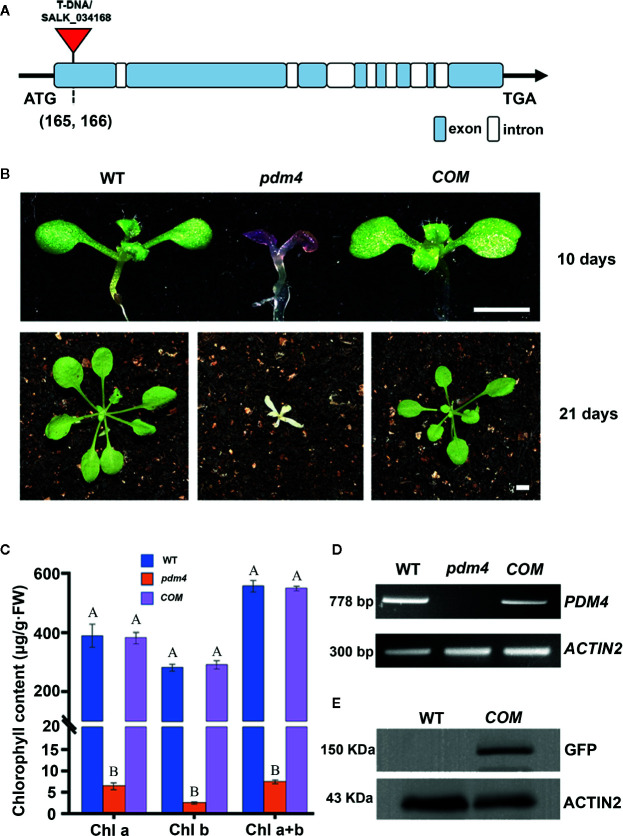
Figure 1.
Identification and characterization of the pdm4 mutant. (A) Gene structure of the PDM4 (AT5G27270). Exons indicated by the wathet boxes, introns by the white boxes, and the T-DNA insertion indicated by the red triangle; ATG represents the initiation codon, and TGA represents the stop codon. (B) Pigment-defective phenotypes and complementation of the pdm4 mutant. The cDNA of the PDM4 was cloned into a binary expression vector with the GFP tag and complementation of the pdm4 mutant (COM). WT, wild type. 10-day-old plants were grown on sucrose-supplemented medium (up lane), and 21-day-old plants were grown in soil (down lane). Scale bar: 3 mm. (C) The chlorophyll content of wild-type, pdm4 and COM. Chlorophyll was extracted from 14-day-old seedlings and quantified. Values given are μg/g fresh weight ± SD (n = 3). Values not connected by the same letters are significantly different (Student’s t test, p < 0.05). The average of three replicates is shown. (D) Reverse transcription PCR analysis. RT-PCR was performed using specific primers for AT5G27270 or ACTIN2. (E) Total proteins from wild-type and COM (15 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis with the anti-GFP. The experiments of (D, E) were repeated three times independently.