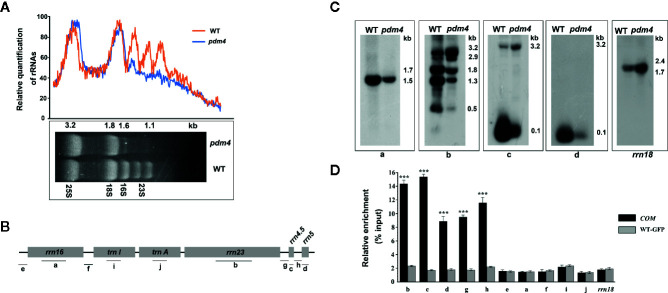
Figure 7.
The chloroplast rRNA processing in pdm4 mutant. (A) The contents of rRNAs in wild type and pdm4. 5 μg of total RNA from 3-week-old wild type and pdm4 seedlings was separated by denaturing gel. 23S* is the breakdown product of the chloroplast 23S rRNA. rRNA was quantified using “ImageJ” software. (B) Diagram of the chloroplast rRNA operon and the locations of the probes (a–d) used for the RNA gel-blot analysis and used for RNA immunoprecipitation analysis (a–j). (C) RNA gel analysis of 16S rRNA (probe a), 23S rRNA (probes b), 4.5S rRNA (probe c), and 5S rRNA (probe d). The sizes of the transcripts (in kb) are shown. The 18S rRNA is shown as a loading control. (D) RNA immunoprecipitation analysis followed by a quantitative PCR assay. Probes b, d, c, a, i, f, and rrn18 are fragments from the 23S rRNA, 5S rRNA, 4.5S rRNA, 16S rRNA, trnI, trnA, and 18S rRNA, respectively and probes e, f, g, h for the intergenic region. The asterisks indicate significant differences between WT-GFP and COM (Student’s t test; ***p < 0.001). Data are means (± SE) obtained from three replicates.