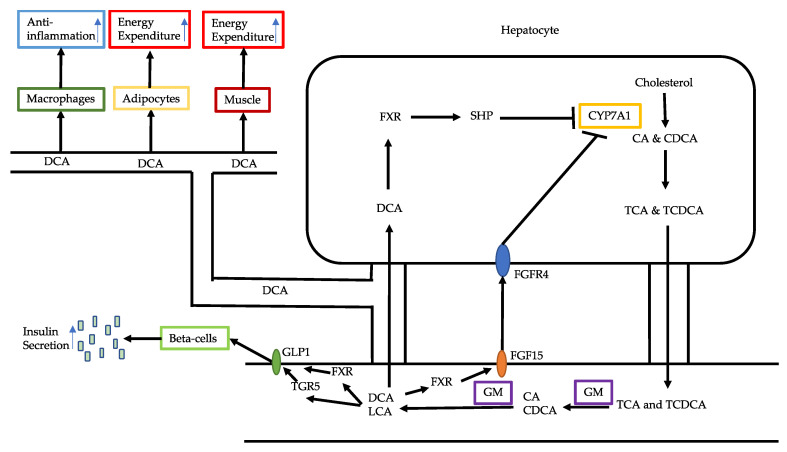
Figure 1.
Bile acids and their receptors in NAFLD. Cholesterol is converted by CYP7A1 into primary bile acids CA and CDCA, which are conjugated and secreted into the intestines. In the intestines, TCA and TCDCA are deconjugated and converted into secondary bile acids DCA and LCA by GM. DCA and LCA stimulates the secretion of intestinal FGF15, which circulates to the liver and binds to FGFR4, causing inhibition of CYP7A1. DCA also circulates into the liver to activate PXR in the liver, which leads to inhibition of SHP, an inhibitor of CYP7A1. DCA stimulates the secretion of intestinal GLP-1 through activation of PXR and TGR5. GLP-1 binds to GLP-1R on beta-cells to stimulate insulin secretion. DCA in circulation can also act on macrophages to exert anti-inflammatory effect and act on adipocytes and muscle cells to increase energy expenditure. Abbreviations: CYP7A1, cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1; CA, cholic acid; CDCA, chenocholic acid; TCA, taurocholic acid; TCDCA, taurochenocholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid; GM, gut microbiota; FGF15, fibroblast growth factor 15; FGFR4, fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; PXR, pregnane X receptor; SHP, small heterodimer partner; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; TGR5, G protein-coupled receptor.