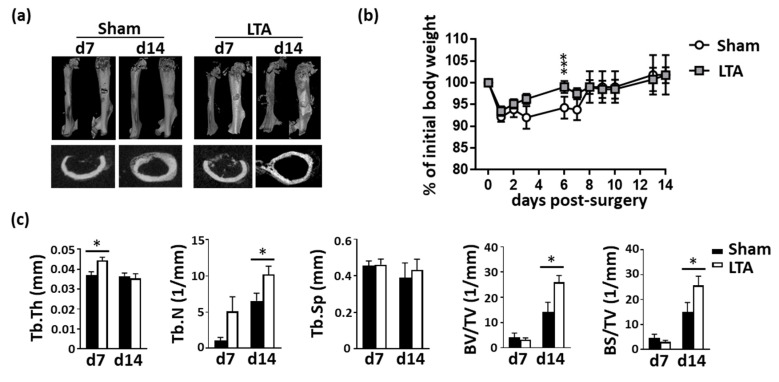
Figure 1.
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) accelerated new bone formation and bone healing in mice with femoral bone defects. (a) Mice with femoral bone defects were subjected to intrafemoral injection of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; sham vehicle control) or LTA. The results of micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) revealed that treatment with LTA (but not the vehicle control) enhanced the bone healing. (b) Body weights were measured daily in mice treated with PBS or LTA. All the results were normalized to the initial weight of each mouse. (c) Quantitative results of micro-CT analysis in mice treated with PBS (n = 5) or LTA (n = 6). Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Analyses were conducted with two-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001. Abbreviations: d, day; Tb.Th, trabecular thickness; Tb.N, trabecular number; Tb.Sp, trabecular spacing; BV, bone volume; TV, tissue volume; BS, bone surface.