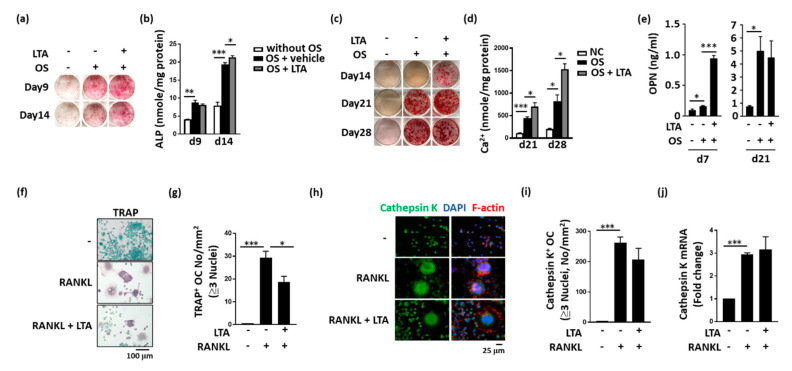
Figure 3.
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) had beneficial effects on bone formation in vitro. (a–d) LTA enhanced alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression and calcium levels during osteoblast (Ob) differentiation. (e) The osteopontin (OPN) concentrations in the cell culture medium were measured by performing enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays at the indicated time points. OPN-expression levels in the LTA-treated group were higher than those in the control group. (f) LTA decreased the differentiation of RAW264.7 cells into tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-positive osteoclast (Ocl)-like cells. (g) Quantitative analysis confirmed that LTA treatment decreased receptor activator of the nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL)-induced differentiation of TRAP-positive Ocl-like cells. (h,i) Immunofluorescence staining confirmed that LTA did not affect RANKL-induced differentiation of cathepsin K-positive Ocl-like cells. (j) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis was performed to measure the mRNA-expression levels of cathepsin K. The data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Analyses were conducted with two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.