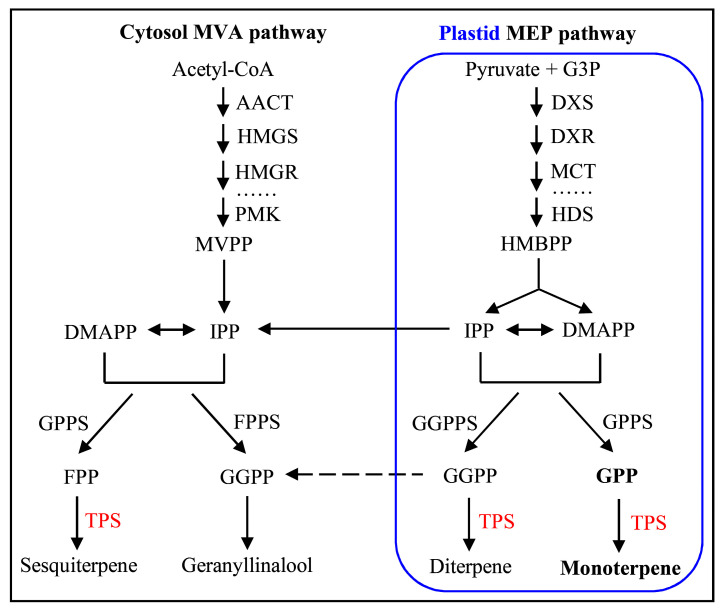
Figure 1.
The pathway of terpene synthase genes responsible for the formation of terpenes in planta [3]. Terpenes are biosynthesized by the cytosol mevalonic acid (MVA) and the plastid methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways, the former giving rise to sesquiterpenes and geranyllinalool, and the latter to monoterpenes and diterpenes. AACT, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; DMAPP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; DXS, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase; FPP, farnesyl pyrophosphate; FPPS, FPP synthase; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate; GGPPS, GGPP synthase; GPP, geranyl pyrophosphate; GPPS, GPP synthase; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate synthase; HMBPP, (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate; HMGR, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase; HMGS, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; MCT, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase; MVPP, mevalonate 5-pyrophosphate; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; TPS, terpene synthase.