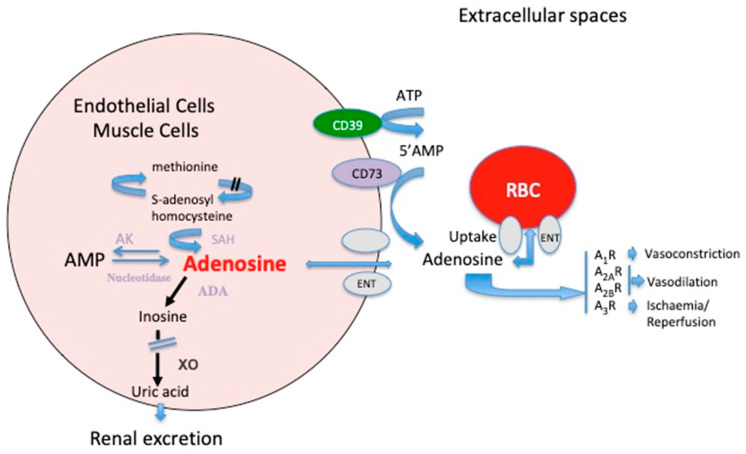
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the adenosine metabolism and its effects on vessels. At the extra cellular level, the main source of adenosine is the dephosphorylation of ATP and AMP via the ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73. In the intracellular spaces, adenosine comes from AMP dephosphorylation though cytosolic nucleotidase. Part of adenosine comes from the methionine cycle. ADA: adenosine deaminase; AK: adenosine kinase; XO: xanthine oxidase; SAH: s-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase; A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R are adenosine receptor subtypes; ENT: equilibrative nucleoside transporter.