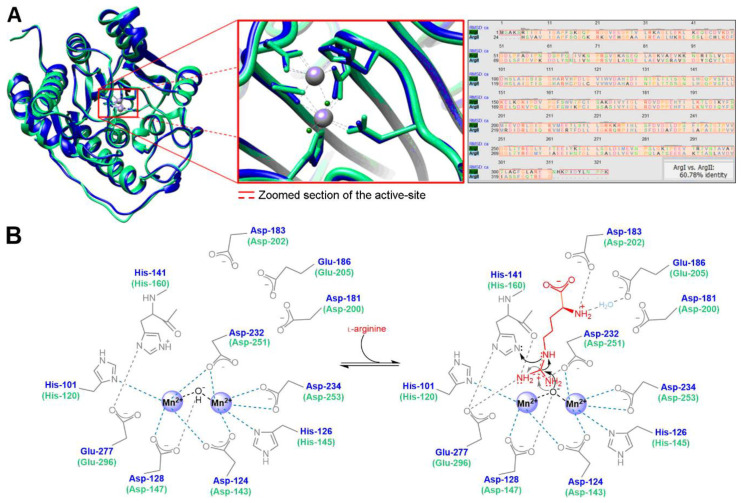
Figure 2.
(A) Superposition of human Arg1 and Arg2 (blue and green color, respectively) subunits and active-sites and amino acid sequence alignment showing the shared homology percentage by both isoforms (molecular graphics and analyses performed with UCSF Chimera [12] using PDB accession codes 2ZAV [13] and 1PQ3 [9]). (B) Schematic overview of the most relevant active-site amino acid residues involved in catalytic plasticity, and proposed L-arginine binding mechanism.