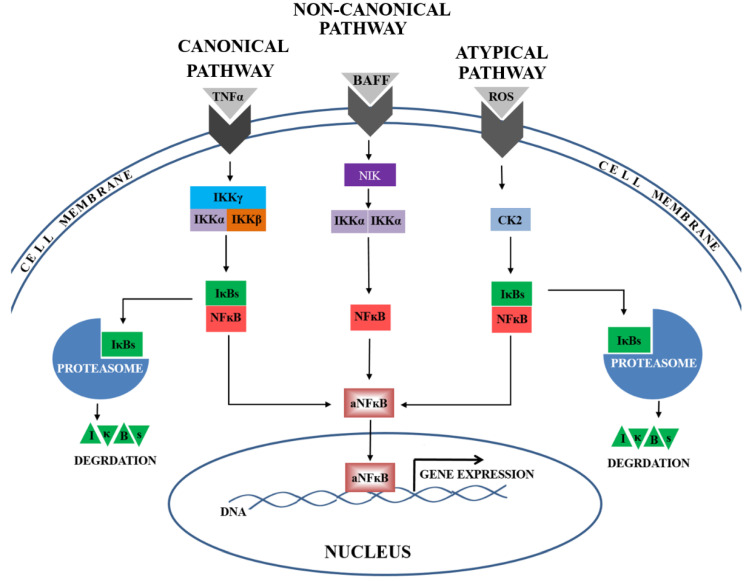
Figure 3.
The canonical, non-canonical, and atypical NFκB signaling pathways are activated by multiple stimulants, e.g., TNF-α, BAFF or ROS. In the canonical pathway, the complex of activators, including: IKKγ, IKKβ, and IKKα, is responsible for NFκB activation by proteolysis one of the following inhibitors (IκBs): IκBα or IκBβ. In the non-canonical pathway, IKKα, supported by NIK, is responsible for NFκB activation. In the atypical pathway, the casein kinase 2 (CK2) mediates IκB (IκBα or IκBβ) degradation in the proteasome. Following the activation, NFκB is rapidly translocated into the nucleus. There, the active form of NFκB (aNFκB) recognizes the consensus sequence in the DNA and regulates the expression of numerous genes.