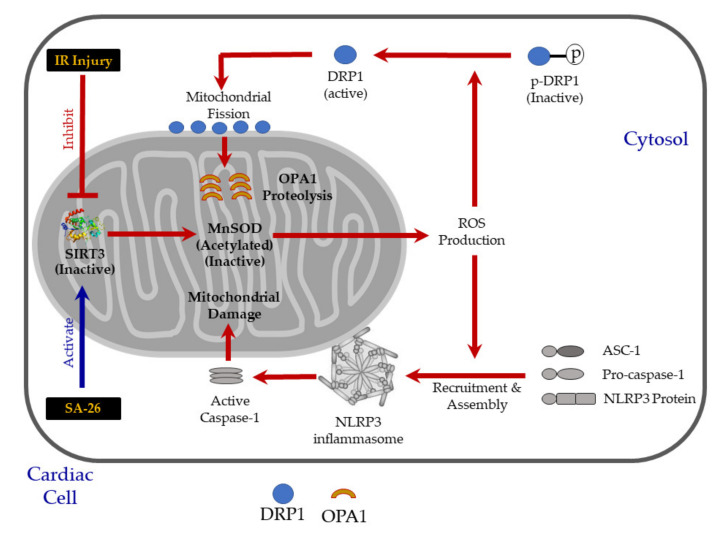
Figure 6.
Conceptual illustration showing the potential cardioprotective role of the EDP surrogate SA-26 against IR injury. Hearts subjected to IR injury showed decreased SIRT3 activity and increased acetylation of MnSOD, suggesting diminished antioxidant capacity. Accordingly, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) burst from damaged mitochondria triggers excessive activation and recruitment of DRP1 on the mitochondrial outer membrane, inducing OPA1 proteolysis which impairs mitochondrial fusion, perturbs cristae structure, and prompts mitochondrial fragmentation. Furthermore, the excessive ROS production from the damaged mitochondria activates the assembly of NLRP3 inflammasome on mitochondrial membrane leading to the activation of caspase-1 which in turn, aggravates mitochondrial damage. Perfusion of hearts with SA-26 during the reperfusion period ameliorates IR injury by maintaining mitochondrial integrity and function. Hearts perfused with SA-26 showed improved SIRT3 activity, enhanced antioxidant capacity and limited oxidative injury. This effect was associated with the inhibition of the assembly and mitochondrial translocation of the detrimental NLRP3 inflammasome and consequently improved postischemic functional recovery.