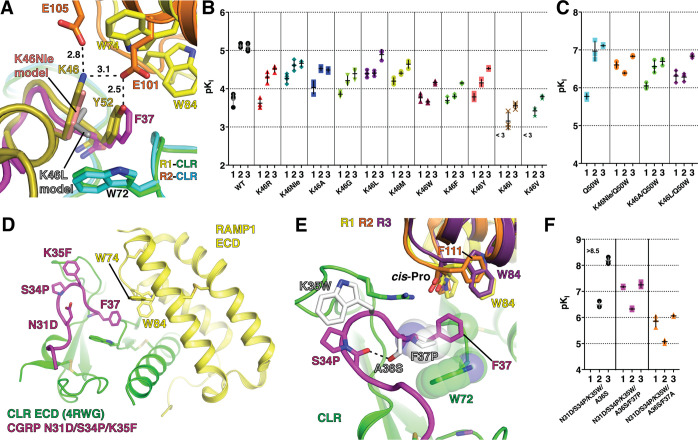
Figure 4.
Probing the ligand selectivity mechanism by AM K46 and CGRP F37 mutagenesis. (A) Detailed view of the pocket over the W72 Trp shelf in superimposed AM-bound RAMP2-CLR ECD [4RWF] and CGRP N31D/S34P/K35F-bound RAMP1-CLR ECD [4RWG] crystal structures. AM position 46 substitutions K46Nle and K46L are modeled and key residues are shown as sticks. (B,C) Scatter plots of mean pKI values from competition FP assays with purified MBP-RAMP-CLR ECD complexes and the indicated AM(37–52) K46 variants in the (B) wild-type or (C) Q50W backgrounds. (D) Crystal structure of CGRP N31D/S34P/K35F-bound MBP-RAMP1-CLR ECD [PDB 4RWG] with MBP omitted. (E) CGRP K35W, A36S, and F37P substitutions are modeled and shown with the indicated RAMP1–3 residues that augment the pocket. RAMP3 is a homology model. (F) Scatter plot of mean pKI values from competition FP assays using purified MBP-RAMP-CLR ECD complexes with the indicated CGRP F37 variants in the N31D/S34P/K35W/A36S background. The high-affinity detection limit of the assay prevented unambiguous determination of the affinity of the N31D/S34P/K35W/A36S variant at the RAMP1 complex. See Table S3 for the pKI values with SEM, selectivity comparisons, and associated statistical analyses.