Figure 10.
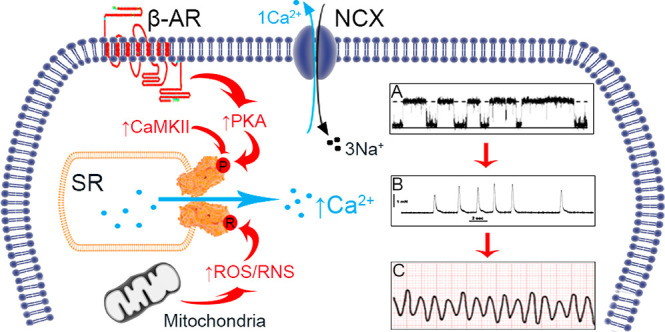
Stress-induced mechanisms of arrythmia. In HF, there is chronic β-AR activity and increased ROS/RNS generation. Vulnerable residues on RyR2 are susceptible to phosphorylation and redox modifications, which increase RyR2 Po (diagram A). In diastole there is pathological SR Ca2+ leak which can activate neighboring NCX, extruding Ca2+ causing sarcolemma depolarization; the generation of DADs and spontaneous contractions (diagram B). Ultimately this may degenerate into ventricular arrythmia (diagram C) and SCD.
