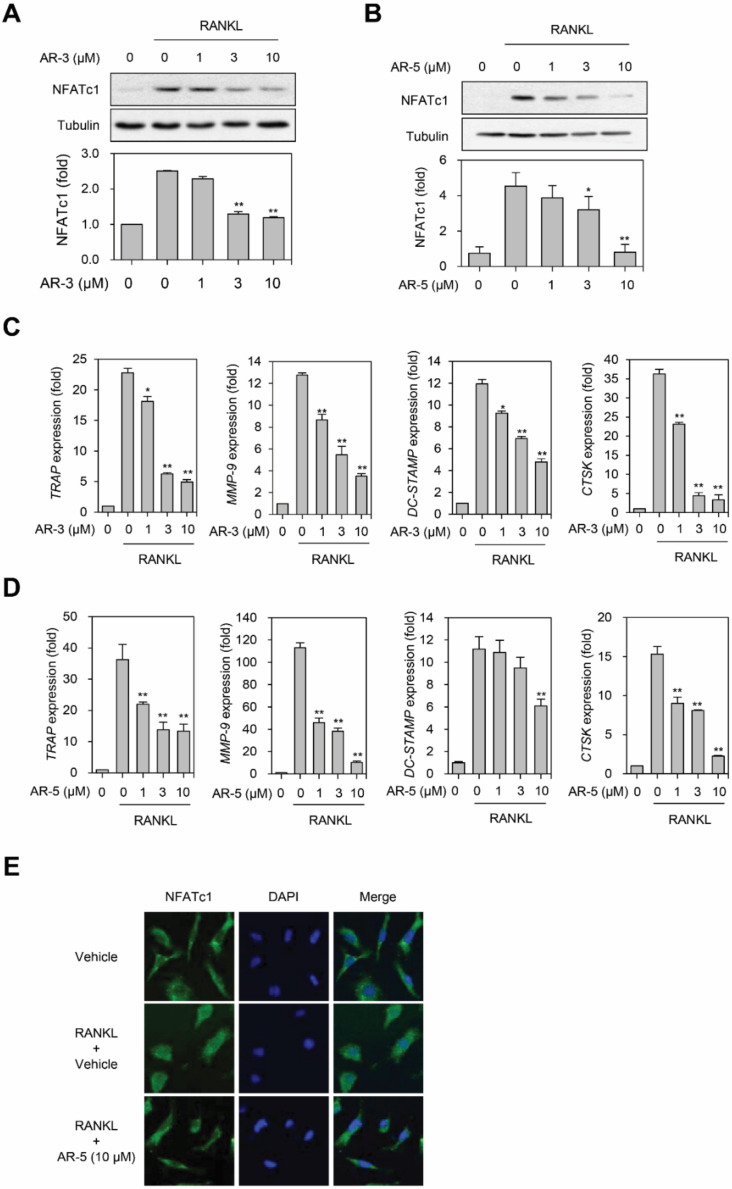
Figure 5.
AR-3 and AR-5 inhibit RANKL-induced NFATc1 activation and its target gene expression. (A,B) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with RANKL in the presence of the indicated concentrations of AR-3 (A) or AR-5 (B) for 48 h. The expression level of NFATc1 was determined by western blotting. Graphs represent densitometry analyses normalized to tubulin (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01, versus vehicle-treated control, n = 3). (C,D) BMMs were incubated with M-CSF and RANKL in the presence of indicated concentrations of AR-3 (C) or AR-5 (D) for four days. Reverse transcription qPCR analysis was performed to quantify the mRNA expression levels of TRAP, MMP-9, DC-STAMP, and CtsK. Data are presented as the mean ± SE (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01, versus the vehicle-treated control; n = 5). (E) BMMs were stimulated with RANKL and M-CSF in the presence or absence of AR-5 (10 µM) for three days. The cells were fixed and stained with an anti-NFATc1 antibody, followed by an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody. DAPI was used to stain nuclei.