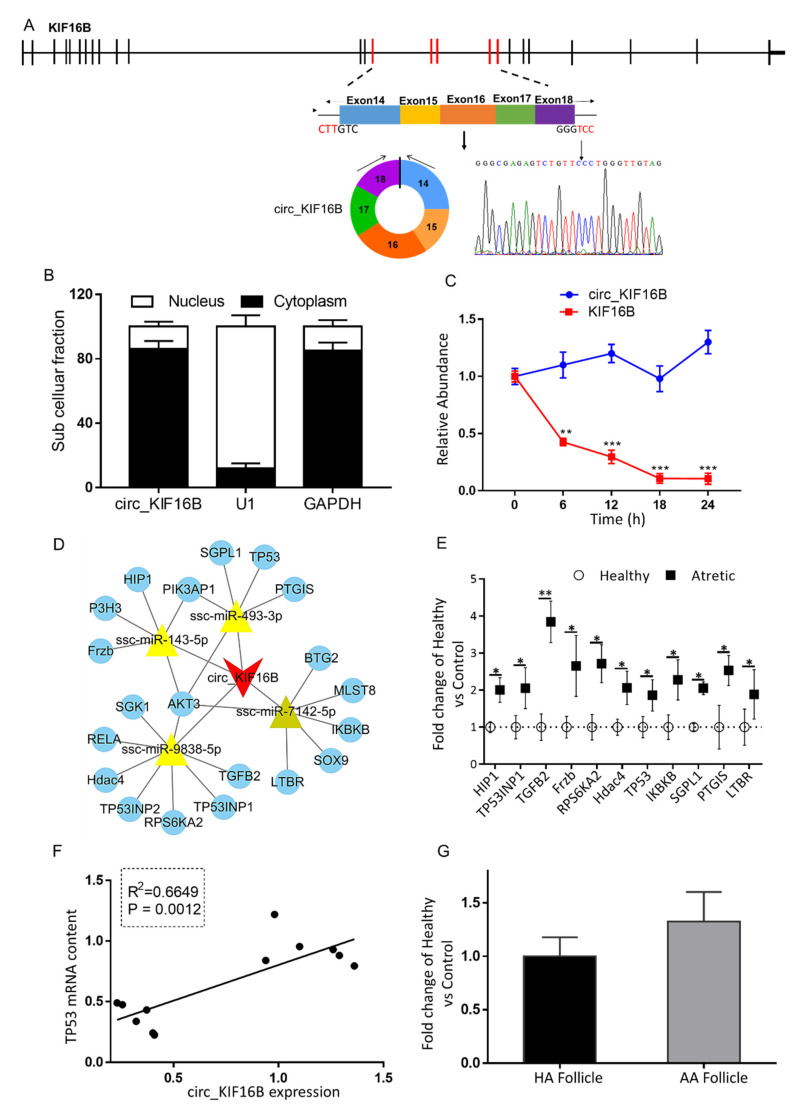
Figure 6.
Characterization and putative role of circ_KIF16B. (A) The genomic loci of circ_KIF16B in the KIF16B gene. The expression of circ_KIF16B was validated by qRT-PCR, followed by Sanger sequencing. Arrows represent divergent primers binding to the genome region of circ_KIF16B. (B) Cellular characterization of circ_KIF16B. Levels of nuclear control transcript (U1), cytoplasmic control transcript (GAPDH and mRNA), and circ_KIF16B were assessed by qRT-PCR in nuclear (n = 3) and cytoplasmic fractions (n = 3) of porcine granulosa cells. Data are presented as a percentage of U1, GAPDH, and circ_KIF16B levels. (C) qRT-PCR for the abundance of circ_KIF16B (blue line, n = 3) and KIF16B mRNA (red line, n = 3) in granulosa cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. (D) A putative ceRNA network of circ_KIF16B constructed by Cytoscape 3.8. The red V shape represents circ_KIF16B, the yellow triangle represents targeted miRNAs, and blue round circles denote targeted mRNAs. (E) qRT-PCR for the abundance of mRNA content of 10 targeted pro-apoptotic genes in granulosa cells of HA (open circles, n = 6) and AA (filled squares, n = 6) follicles. (F) Correlation of expression levels of circ_KIF16B and TP53. (G) circ_KIF16B expression in cumulus cells of HA (black bar, n = 6) and AA follicles (grey bar, n = 6), as measured by qRT-PCR. Gene expression, as fold change of AA over HA follicles, with no change, was indicated as 1. KIF16B, kinesin family member 16B; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. Follicles were isolated in batches at three different time points, each batch containing 15–20 ovaries.