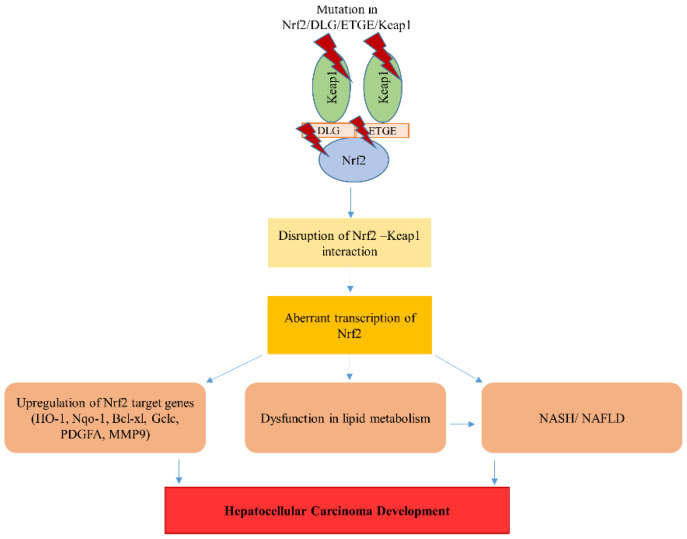
Figure 2.
Mutations in NRF2 or Keap1 cause aberrant accumulation of NRF2 in the nucleus that leads to an increase in NRF2 target genes. This aberrant activation of NRF2 dysregulates the lipid metabolism responsible for the non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)/non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) pathology. Consequently, these events lead to the development of HCC.