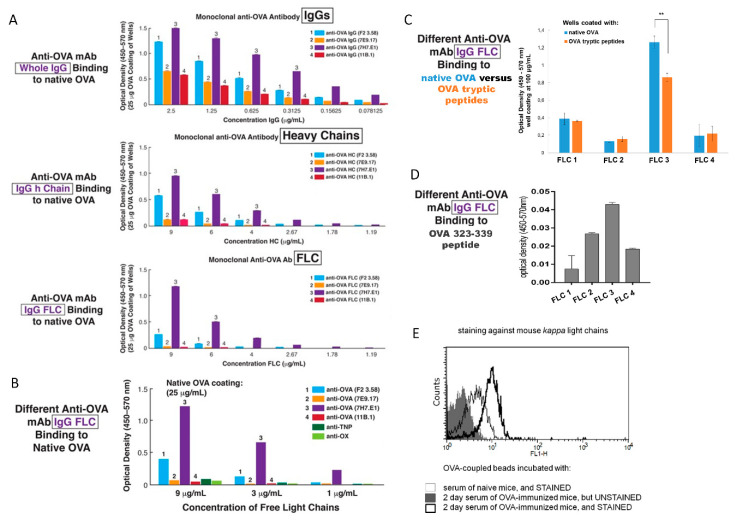
Figure 6.
ELISA assays to assess the ability of four different monoclonal anti-OVA Ab-derived free light chains (FLC) to bind to native OVA, OVA tryptic peptides, and OVA 323-339 peptide, as well as flow cytometry analysis of anti-OVA Ab FLC in 2-day immune serum. (A) Binding to native OVA by serial dilutions of four different monoclonal anti-OVA Ab-derived FLC and Ab heavy chains, vs. the whole IgGs, shows significant binding with a particular mAb and similar strength with a given mAb and its derived heavy and light chains. (B) Binding of various monoclonal anti-OVA Ab FLC to native OVA compared to binding of control anti-OX and anti-TNP hapten-specific mAb shows the Ag specificity of the anti-OVA Ab FLC binding. (C) Comparison of binding of four monoclonal anti-OVA Ab-derived FLC to either native OVA or OVA tryptic peptides, showing a difference only in the case of FLC 3. The two-tailed Student t test, ** p < 0.01. (D) Binding of four monoclonal anti-OVA Ab-derived FLC to OVA 323-339 antigenic determinant. (E) The presence of OVA Ag-specific Ab FLC in 2-day serum of OVA-immunized mice (thick black line) was confirmed by flow cytometry, as compared to serum of control non-immunized mice (thin black line). n = 3 wells or samples in each experimental repetition.