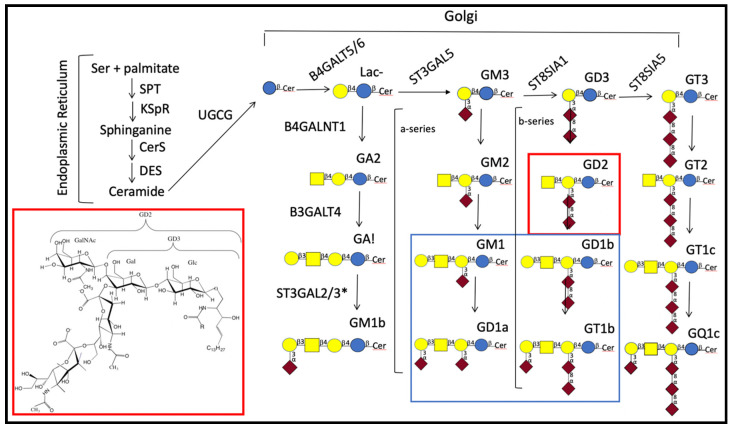
Figure 1.
Synthetic pathways for common central nervous system (CNS) gangliosides. Major CNS gangliosides are enclosed by the rectangle outlined in blue and the structure and place of GD2 in the synthesis of gangliosides by red;  —glucose;
—glucose;  —galactose;
—galactose;  —N-acetylgalactosamine; and
—N-acetylgalactosamine; and  —sialic acid [11]. GA1, GA2, and GA3 indicate asialylated gangliosides. Nomenclature used for ganglioside series gangliosides was developed by Svennerholm [12]. Brackets indicate gangliosides that are in the a-series (one sialic residue linked ±2–3 to the galactose linked β1–4 to glucose) or in the b-series (two sialosyl residues linked to the galactose as shown). Gene abbreviations are those of the Human Genome Organization (HUGO) gene nomenclature committee (https://www.genenames.org/tools/multi-symbol-checker/). Enzymes indicated are: B4GALT5/B4GALT6 [13,14], UDP-galactose: glucosyceramide β1–4 galactosyl transferase (lactosylceramide synthase); B4GALNT1, UDP-GalNAc:LacCer/GM3/GD3/GT3 β1–4 N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase (ganglioside GA2, GM2, GD2, synthase); B3GALT4, UDP-galactose:GA2/GM2/GD2/GT2 β1–3 galactosyl transferase (ganglioside GA1, GM1a, GD1b, and GT1c synthase); CerS, ceramide synthase; DES, dihydroceramide desaturase; UGCG, UDP-glucose:ceramide β1-1′-glucosyl transferase; KSpR, 3-ketosphinganine reductase; SPT, serine-palmitoyl transferase; ST3GAL5, CMP-sialic acid:lactosylceramide α2–3 sialyltransferase (GM3 synthase); ST8SIA1, CMP-sialic acid:GM3 α2–8-sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase); ST8SIA5, CMP-sialic acid:GD3 α2–8-sialyltransferase (GT3 synthase). * ST3GAL2/3 are needed in mice for synthesis of D1a and T1b [15], but the specificity of these enzymes in humans is still under study [16]. For a discussion of similarities and differences in genes needed for ganglioside synthesis in mice and humans see Schnaar [17]. For characterization of GM1b see [18].
—sialic acid [11]. GA1, GA2, and GA3 indicate asialylated gangliosides. Nomenclature used for ganglioside series gangliosides was developed by Svennerholm [12]. Brackets indicate gangliosides that are in the a-series (one sialic residue linked ±2–3 to the galactose linked β1–4 to glucose) or in the b-series (two sialosyl residues linked to the galactose as shown). Gene abbreviations are those of the Human Genome Organization (HUGO) gene nomenclature committee (https://www.genenames.org/tools/multi-symbol-checker/). Enzymes indicated are: B4GALT5/B4GALT6 [13,14], UDP-galactose: glucosyceramide β1–4 galactosyl transferase (lactosylceramide synthase); B4GALNT1, UDP-GalNAc:LacCer/GM3/GD3/GT3 β1–4 N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase (ganglioside GA2, GM2, GD2, synthase); B3GALT4, UDP-galactose:GA2/GM2/GD2/GT2 β1–3 galactosyl transferase (ganglioside GA1, GM1a, GD1b, and GT1c synthase); CerS, ceramide synthase; DES, dihydroceramide desaturase; UGCG, UDP-glucose:ceramide β1-1′-glucosyl transferase; KSpR, 3-ketosphinganine reductase; SPT, serine-palmitoyl transferase; ST3GAL5, CMP-sialic acid:lactosylceramide α2–3 sialyltransferase (GM3 synthase); ST8SIA1, CMP-sialic acid:GM3 α2–8-sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase); ST8SIA5, CMP-sialic acid:GD3 α2–8-sialyltransferase (GT3 synthase). * ST3GAL2/3 are needed in mice for synthesis of D1a and T1b [15], but the specificity of these enzymes in humans is still under study [16]. For a discussion of similarities and differences in genes needed for ganglioside synthesis in mice and humans see Schnaar [17]. For characterization of GM1b see [18].